What Is A Cannabis Use Disorder
Cannabis Use Disorder is the medical term for a spectrum of patterns of cannabis use leading to significant impairment or distress, including health problems, persistent or increasing use, and failure to meet major responsibilities at work, school, or home. It can range from mild, to moderate, to severe, depending upon how many of the symptoms described below are present. Individuals must show at least 2 symptoms over a 12-month period to receive the diagnosis of a Cannabis Use Disorder. More information on Cannabis Use Disorder can be found in the American Psychiatric Associations Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition. If you have questions about Cannabis Use Disorder, please discuss with your healthcare professional.
Which Is More Addictive
If were talking merely physical dependence and risk of death, alcohol is far more addictive. However, substance use disorders are defined as when a persons use of alcohol or another substance leads to health issues or problems with work, school, or home.
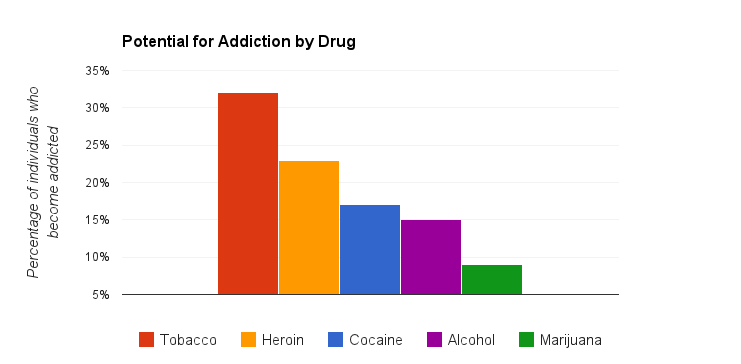
Asking which substance is more addictive is like choosing the lesser of two evils no one wins. Marijuana addiction is a very real thing, and about 9 percent of people who use marijuana will develop a .
The addictive quality of marijuana is also changing as the potency of weed is much higher now than it was even just 20 years ago, and there is no reliable way to know how much THC is in pot, but the potency of alcohol is strictly regulated.
Both substances, when abused, can be addictive and lead to social, health, and personal consequences. So instead of asking which is more addictive, its probably a good rule of thumb to consider getting help for yourself or a loved one if quality of life is getting worse because of the use of marijuana or alcohol.
If you or a loved one is struggling with an addiction to alcohol, marijuana, or another substance the treatment professionals at Genesis Recovery can help. We are waiting for your call and look forward to speaking with you.
Do you or a loved one need help?
Officially Marijuana Is More Dangerous
Although eight states have passed laws legalizing recreational marijuana use, and 29 states have legalized medical marijuana, federal law still labels marijuana as an illegal substance.
The DEA classifies marijuana as a Schedule 1 drug, defined as having no accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Other Schedule 1 drugs include LSD and heroin.
On the other hand, Schedule 2 drugs, which include crystal methamphetamine and cocaine, have been accepted as medical treatments in the United States.
Prescription opioids, which include morphine, fall into this category of drugs legal when prescribed by medical personnel.
Dr. Thomas Strouse, medical director of the Stewart and Lynda Resnick Neuropsychiatric Hospital at the University of California, Los Angeles , thinks the classifications are a bit ridiculous.
Although marijuana can cause health problems if used in excess, he said, there are no known cases of somebody dying from a marijuana overdose. The same cannot be said for opioids.
The CDC reports that overdose deaths from opioids have quadrupled since 1999. In 2015, more than 15,000 Americans died from overdoses involving prescription opioids. Those prescription pills now account for nearly half of all U.S. overdoses from opioids.
In addition, an average of 1,000 Americans are treated in emergency rooms every day for misusing prescription pills.
Overall, the use of prescription medication far outdistances the use of marijuana.
But is it healthy for you?
Read Also: How To Fight Marijuana Addiction
Can Medical Marijuana Lead To Addiction
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, marijuana is the most commonly abused illicit drug in the United States. The Drug Enforcement Administration classifies marijuana as a Schedule I drug, defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse.
Despite this definition of marijuana, there is some evidence that the drug can be therapeutic. It can help with pain management and is often used as palliative care for chronic conditions like cancer. Currently, 23 states allow recreational or medical use of marijuana, including Pennsylvania.
If youre considering medical marijuana as a treatment, one of your concerns may be the possibility of addiction. Heres what we know about the potential for addiction with this drug. As always, you should talk to your doctor to determine which treatment is best for you.
Classification And Medical Use
The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration classified marijuana as a Schedule I drug in 1970, which means that it is in a category characterized by a high potential for abuse and no acceptable medical application. This puts marijuana in the same class as heroin, LSD, peyote, methaqualone, and ecstasy.
This classification contradicts information from other sources about the medicinal uses of marijuana that has precipitated the medical marijuana industrys presence in several states.
According to NLM, marijuana contains two main cannabinoids: THC and CBD. These chemicals have been isolated for use in some medicines to treat nausea and increase appetite in cancer and AIDS patients. CBD has also been used to treat childhood epilepsy.
Some people are turning to marijuana as a substitute for opioid painkillers because of opioids highly addictive properties and the associated dangers of overdose. A report published in the Journal of Psychoactive Drugs indicates that researchers are beginning to look at the potential risks and benefits of medical marijuana as a way to reduce tolerance to and withdrawal from opioids in patients with chronic pain conditions.
You May Like: How To Convince An Addict To Go To Rehab
Withdrawal Symptoms From Marijuana Include The Following:
- Irritability
- Tremors
- Depression
The presence of these symptoms when marijuana use has stopped can indicate that a dependency has developed in the body. This means the body has become acclimated to having marijuana present, and the brain is signaling to ingest more of the drug to get relief from these symptoms.
These symptoms could last anywhere from a day to a few weeks, depending on how long a person has been using marijuana and how much of the drug they have been consuming.
What Do We Know About Addiction To Cannabis
Research has shown that using cannabis regularly and over a long time , especially when use begins in early adolescence , can cause changes in the way the brain and body respond to cannabis and lead to problems with cannabis use and addictionFootnote 8
Addiction can occur at any age, but the chances are higher while the brain is still developing, which can continue until around 25 years of age.Footnote 4 As well, the younger an individual is when they begin using cannabis, the higher their risk of health problems, including addiction and other mental health issues including psychosis, schizophrenia, social anxiety, and depression.Footnote 9
Recent US national data estimate that 1 in 3 individuals who use cannabis will develop a range of problems with cannabis use that will have an impact on their daily lives.Footnote 10
The term Cannabis Use Disorder encompasses the concept of a range of problems with cannabis use. When using cannabis has a significant impact on daily life this can be considered an addiction to cannabis.
You May Like: How To Break Phone Addiction
Risk Of Using Other Drugs
Researchers disagree on whether marijuana is a gateway drug the idea that marijuana use leads a person to use other more dangerous drugs, like cocaine or heroin.1,2 However, there is limited evidence suggesting that using marijuana increases the risk of using other drugs.3
Most people who use marijuana do not go on to use other, harder drugs.4 People who use marijuana and do go on to use other drugs may have a higher risk of dependence or addiction to those drugs, especially if they started using marijuana at an early age and use it frequently.4-6
People of any age, sex, or economic status can develop a substance use disorder for marijuana or other drugs. The following things can affect the likelihood of substance use disorder6:
- Family history
- Having another mental health illness
- Peer pressure
- Socioeconomic status
Signs Of Marijuana Addiction
Someone who becomes addicted or dependent upon marijuana will likely display some of the classic behavioral symptoms of addiction, which include:
- They will begin to need increasingly larger amounts.
- They will spend more time thinking about using.
- Substance use will begin to take a central role in their life.
- They will spend more time and money acquiring more marijuana.
- They will become irritable or agitated if they run out.
- As negative consequences mount, they will continue to use.
- They will deny claims from those close to them that they have changed.
Two of the most common signs of cannabis use disorder are physical dependence and withdrawal.
You May Like: Can You Get Addicted To Nicotine Gum
Theoretical Model Of Addiction
Koob and Volkow define drug addiction as a chronically relapsing disorder marked by compulsive drug seeking and intake, loss of control in limiting intake, and the emergence of a negative emotional state when access to a drug is prevented. This model proposes three stages of addiction with disturbances in three major neurocircuits: the binge/intoxication stage driven by changes in the basal ganglia the withdrawal/negative affect stage driven by changes in the extended amygdala and the preoccupation/anticipation driven by changes in the prefrontal cortex . Within these domains, Koob and Volkow describe neuroadaptations in 18 subsystems including the ascending mesocorticolimbic dopamine system, corticotropin-releasing factor in the central nucleus of the amygdala, and corticostriatal glutamate projections.
Scale Of Addiction: What Drugs Are More Addictive Than Others
There is no straightforward answer to the question of which drug is most addictive. The subject of addiction in general does not come in black-and-white terms. Theres a lot of gray area when it comes to figuring out if a person has an addiction disorder, and the very definition of the word addiction leaves a lot of room for interpretation.
Most addiction experts agree that theres both a physical and a psychological aspect to addiction. Addictive substances have physical effects on the brain and cause pleasurable sensations that prime the brains pleasure-reward response. At the same time, a persons stress levels, life satisfaction, attitudes about drug use, and the presence of other mental illnesses are all considered to be factors in the development of an addiction disorder. People can even become addicted to substances that are not considered to be physically addictive because they can form an emotional attachment to the drug and any kind of intoxicant will cause the brain to associate that drug with a pleasure reward.
There is therefore no definitive way to measure how addictive a drug is. However, experts and researchers have found way to rank common drugs for addictiveness based on five factors:
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Being Addicted To Technology
Other Faqs About Marijuana
- Brick: A large, compacted block of marijuana
Its difficult to say whether or not . It depends on a few factors. First and foremost, your mental state and the environment youre in when using marijuana play a big role in how you react. Marijuana and anxiety can go hand-in-hand for some people. You may not get a pleasant or relaxing experience when using it. In fact, your experience could be quite the opposite. Many people feel that marijuana can bring symptoms of anxiety or heighten their existing anxiety, particularly if they use it in a situation that isnt pleasant or trying to conceal their use of the drug.
For more information on how you or a loved one can begin on the road to a marijuana-free life, call The Recovery Village. With an abundance of rehab centers located nationwide, our treatment teams can help you gain the skills needed to live your life without relying on any sort of substance. Our representatives are eager to answer any questions you may have about addiction treatment and recovery. Each call is free and confidential.
Tobacco Smoking Among Marijuana Users
Like users of other drugs of abuse, regular marijuana users have a higher rate of tobacco use than the general population approximately 50 percent of heavy cannabis users also smoke tobacco . Moreover, many adolescents and, to a lesser extent, adults use tobacco and marijuana together, either mixing the substances, smoking blunts , or smoking one immediately after the other.
At least one study suggests that, among cannabis-dependent individuals, tobacco smokers have worse psychosocial problems and poorer cannabis cessation outcomes . Whether this indicates that treatments for marijuana dependence should simultaneously address tobacco smoking is not clear. No clinical studies have focused on this issue. However, research suggests that treatment that promotes smoking cessation does not disrupt alcohol abstinence and may actually enhance the likelihood of longer-term sobriety .
Should we encourage individuals trying to quit marijuana use to try also to quit tobacco? Certainly we should discuss this option with clients, as tobacco abstinence may make marijuana abstinence easier and increase chances of maintaining marijuana abstinence for a longer term. However, as with treatments for other substance dependence disorders, mandating tobacco cessation as a treatment goal might create a barrier to treatment seeking or trigger treatment dropout.
Read Also: What Is The Best Treatment For Opiate Addiction
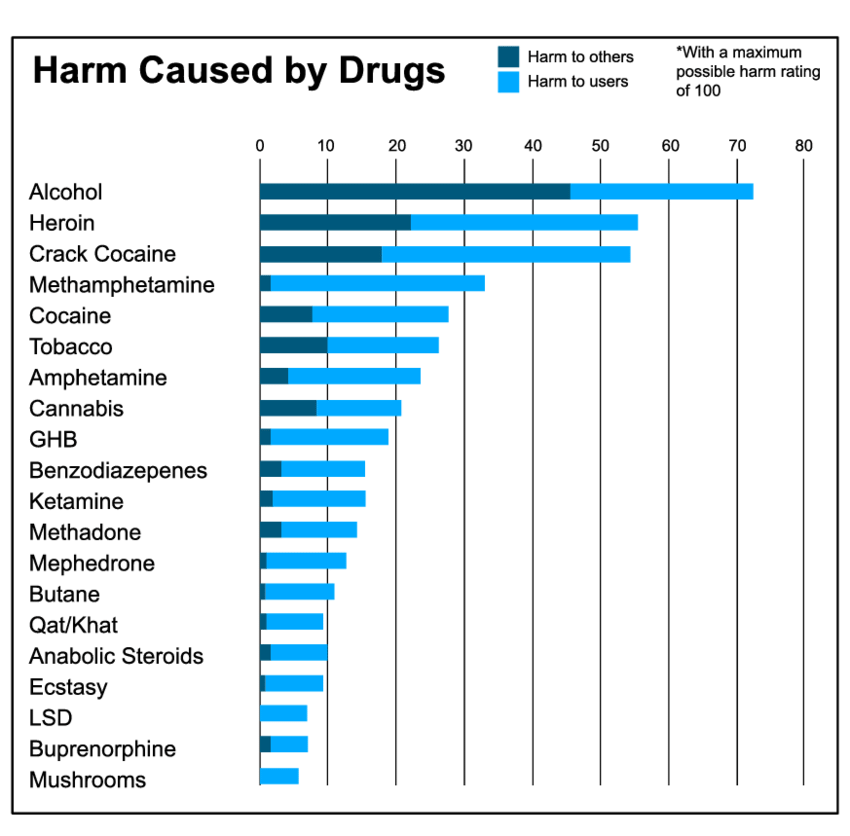
A Snapshot Of The Dangers Of Marijuana Compared To Other Common Drugs
by SkipShoe | Mar 18, 2015 | Cannabis Research, |
One of the biggest objections people have to legalizing marijuana is that our culture has taught us that marijuana is a very dangerous and deadly substance. Consistent with this teaching, the US federal government has prohibited marijuana by classifying it as a Schedule 1 substance the same as heroin.
Is marijuana really dangerous or is that just a myth passed down across generations? In the graph created for this blog post, I mapped the relative riskiness of a substance against the number of deaths attributed to the substance each year. Risk vs. Deaths seems like a pretty good way to determine how dangerous a drug really is. From there, we can compare marijuana to other commonly abused substances legal and otherwise.
Comparing the death rates for common drugs vs. the ranked danger/risks of those drugs
In the graph shown above, the most deadly drugs are in the right hand side of the diagram. The riskiest drugs are in the top two quadrants. These risk factors were chosen to represent key risk dimensions that follow from drug abuse. The bottom left represents the drugs with the lowest risk and the lowest death rate.
UCSF and NIDA researchers ranked the risk of different substances
A good representation of the risk data is shown in the graph above.
References:
shares the data on the NIDA/UCSF risk factor comparison.
Different Methods Of Use
When marijuana is inhaled, the active substance moves rapidly into the lungs and then through the bloodstream. The substance is carried to the brain and other areas of the body. Then, it is rapidly absorbed.
When marijuana is smoked, the effects of the drug begin to take hold within a couple of minutes. They can last for hours, depending on the persons tolerance to the drug.
Also Check: How To Help Someone With Heroin Addiction
Is Marijuana More Or Less Addictive Than Other Drugs
An individuals risk for developing an addiction to marijuana is influenced by many factors, such as personal or family history of substance abuse, adverse childhood traumas, social and environmental factors, and the acceptability of marijuana use in their social groups.
While marijuana may not cause the same level of physical dependence as opioids or meth, it can lead to abuse and psychological dependence. People should carefully consider their risk factors before turning to marijuana for treatment of medical conditions or recreational use.
Comparison With Other Substances
All substances that affect the mind carry their own set of risks and harms, some unique to the substance. The most well-established, long term harm of regular cannabis use is addiction. It is often difficult to compare risks and harms between substances. Nevertheless, based on what is currently known, the risk of cannabis addiction is lower than the risk of addiction to alcohol, tobacco or opioids. And, unlike substances such as alcohol or opioids where overdoses may be fatal, a cannabis overdose is not fatal.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Are Addicted
Alcohol Is One Of The Most Addictive Drugs
Related Reading
Dependence
Although the typical view of cocaine is that its very addictive, its dependence level is not as high as either nicotine or heroin. Even though people do experience a euphoric rush from this drug, fewer will actually develop an addiction. Relapse rates are also significantly lower due to an easier withdrawal and less intense cravings. However, these rates tend to be higher for the cheaper cocaine derivative known as crack cocaine.
Withdrawal
Intensity of withdrawal symptoms for cocaine is considered to be the lowest out of all four drugs discussed here. In fact, there are often no observable physical symptoms associated with cocaine withdrawal. Instead, victims tend to experience simple fatigue, malaise, depression, agitation, restlessness, and a general slowing of activity. Cravings can still be very intense during the worst of the withdrawal, but chronic users often quit because the high has started to produce unpleasant effects.
Tolerance
Surprisingly, tolerance to cocaine is also lower on the spectrum than heroin, nicotine, or alcohol. This is likely why its dependence level is not as high as expected, as tolerance and addiction are closely linked.
Reinforcement
Intoxication
The cocaine high is not as noticeable as heroin or alcohol intoxication. It often gives people a serious boost of energy and may cause them to become very active and talkative. They may actually appear to simply be in a very good mood.
