Introducing The Human Brain
The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. This three-pound mass of gray and white matter sits at the center of all human activityyou need it to drive a car, to enjoy a meal, to breathe, to create an artistic masterpiece, and to enjoy everyday activities. The brain regulates your body’s basic functions, enables you to interpret and respond to everything you experience, and shapes your behavior. In short, your brain is youeverything you think and feel, and who you are.
Which Drugs Kill Brain Cells
Different drugs can have neurotoxic and destructive effects on brain cells. Substances that are associated with neurological damage include but are not limited to alcohol, heroin, amphetamines, marijuana, opioids, inhalants, and cocaine.1,2,5
Drugs can damage brain cells through several mechanisms. Psychostimulants and alcohol disrupt the integrity of the blood-brain barrier , which can change the functioning of your brain cells due to increased permeability . Increased permeability means that toxins can more easily cross the BBB.7
Other substances, including alcohol and inhalants, can cause injury to brain cells due to the way they damage the protective sheaths, known as myelin, that surround nerve fibers. This can cause damage like that which occurs in neurological diseases like multiple sclerosis . This type of damage can affect your thinking, movement, vision, and hearing. The neurological symptoms people experience in this case can range from mild to severe.8,9
The Psychology Behind Alcohol Addiction
Even drinking one beer can have a noticeable influence on a persons mood. Thats because drinking releases endorphins – happy hormones – into your bloodstream. Drinking causes people to feel happy, energized, and excited. It can be quite euphoric for people who dont usually feel this way normally. However, alcohol is a depressant, so those happy feelings arent permanent. Regular drinking causes fatigue, restlessness, and depression. This causes a constant up and down relationship with drinking. The addict is constantly chasing that happy feeling, while the unhappy feelings intensify each time they sober up. In other words, alcohol is both a stimulant and a sedative to the brain. It can even begin to alter a persons thought patterns when theyre sober, leading to misguided thoughts like:
- Im only fun when I drink.
- I cant handle this party unless I drink.
- People like me better when Im drunk.
- The only way Ill make new friends is if I drink.
- Ill just drink tonight, and then everything will be better tomorrow.
An alcoholic begins to associate drinking with who they are. If someone believes they are only capable of love and attention when theyre altered by alcohol, it can become even harder to seek help.
Also Check: How To Avoid Xanax Addiction
Looking For A Place To Start
Reach out to a treatment provider for free today.
- About
Krystina Murray has received a B.A. in English at Georgia State University, has over 5 years of professional writing and editing experience, and over 15 years of overall writing experience. She enjoys traveling, fitness, crafting, and spreading awareness of addiction recovery to help people transform their lives.
- LiveScience.com. Pappas, Stephanie. . This Is Your Brain On Drugs . Retrieved On June 18, 2019 at
- LiveScience.com. Saplakoglu, Yasemin. . How Drug Addiction Hijacks The Brian. Retrieved On June 18, 2019 at
- Neuroceters.com. . Neuroceters.com. . Whats The Difference Between Biofeedback And Neurofeedback? Retrieved On June 18, 2019 at
- NCIB.com. Dimeff, Linda. Linehan, Marsha. . Dialectical Behavior Therapy For Substance Abuse. Retrieved On June 18, 2019 at
- NCIB.com. Gray, Sarah. . An Overview of The Use Of Neurofeedback Biofeedback For The Treatment Of Symptoms Of Traumatic Brain Injury In Military And Civilian Populations. Retrieved On June 18, 2019 at
Clinically Reviewed:
David Hampton
- About
What Can Alcohol Abuse Do To The Brain
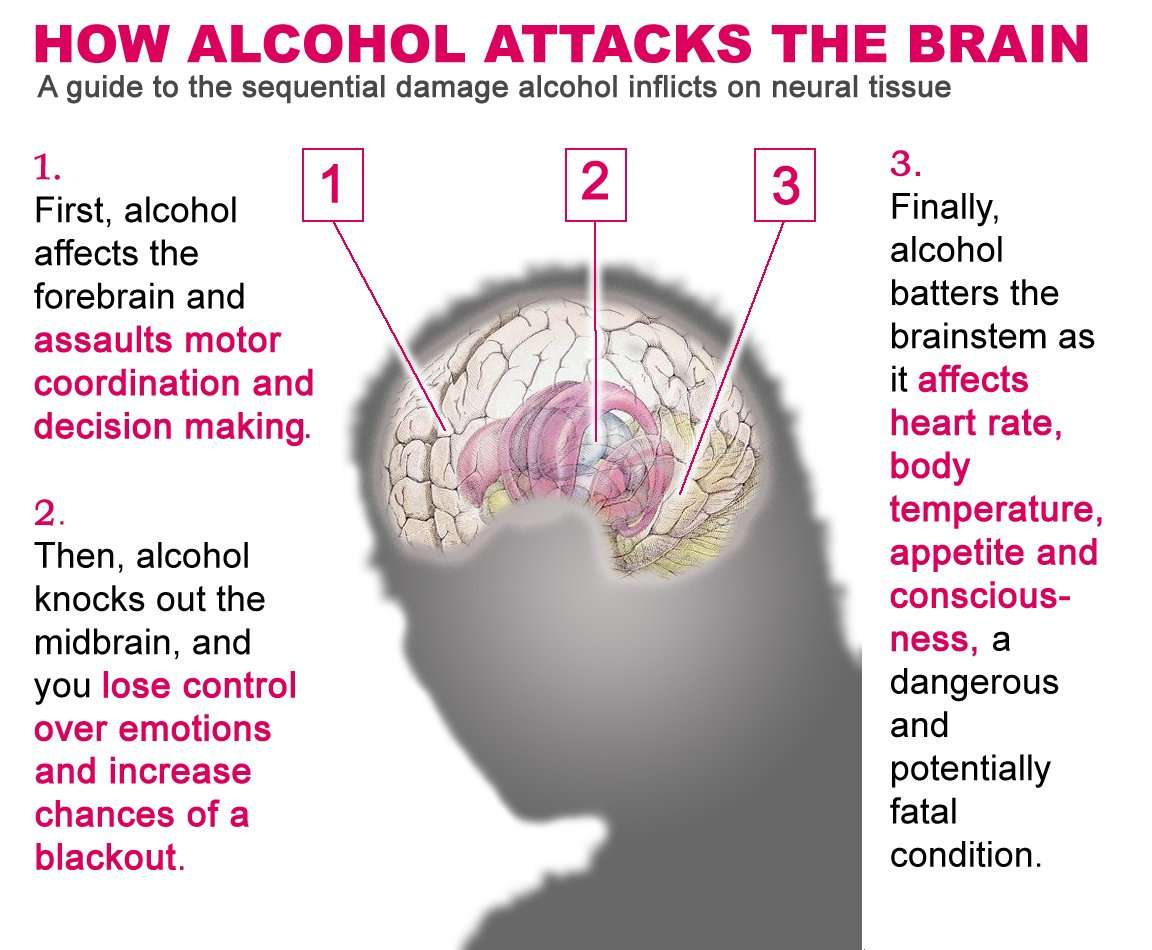
Alcohol is an irritant to all body tissue, from where it comes in to where it goes out. Alcohol does kill brain cells. Some of those cells can be regenerated over time. In the meantime, the existing nerve cells branch out to compensate for the lost functions. This damage may be permanent. Moreover, after a certain age, the connections between neurons begin to prune back. In a brain damaged by alcohol, we may see early-onset dementia.Age makes a difference. The brain is developing until about age 26. This is especially true between the ages of 13 and 26, when theres explosive growth in the prefrontal cortex. People that start drinking heavily at this time are more prone to cognitive problems like impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, anxiety and depression.
Read Also: How To Talk To Addict In Denial
Alcohol Poisoning & Overdose
According to the CDC, an average of 6 people die every day in the U.S. from alcohol poisoning. Many of those deaths are as a result of binge drinking and are not from long-term alcohol use. Just one instance of excessive alcohol intake can result in an overdose, which may lead to brain damage or death.
Binge drinking means to consume a large amount of alcohol in a short period of time and is one of the most common causes of alcohol poisoning. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism states binge drinking occurs when an individuals blood alcohol content is at .08 or higher, which is the threshold for legal intoxication in many states.
An overdose happens when more alcohol is consumed than the body can process, causing a toxic build-up. The extreme depressant effect of this much alcohol can cause irregular heartbeat, dangerously low body temperature, and slowed or stopped breathing.
The Mayo Clinic website lists possible indications of alcohol poisoning including confusion, vomiting, seizures, extremely slow breathing , irregular breathing , bluish or pale skin, hypothermia, and unconsciousness. An alcohol overdose is a medical emergency. If suspected, summon help immediately.
How Alcohol Affects The Brain Dopamine And The Brain
The brain contains neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that transmit signals between brain cells and send information throughout the body. Dopamine is one of those chemical messengers and is strongly impacted by the presence of alcohol. Centered in the motivation, pleasure, and reward center of the brain, dopamine levels influence our mood. Higher levels of dopamine make us feel happier, more motivated and raise our self-esteem. When dopamine levels are low, we may feel depressed and unmotivated.
Dopamine levels naturally increase when we experience something pleasurable, like eating something delicious, exercising, spending time with friends, or receiving positive feedback on a work or school project. Higher levels of dopamine make us feel happy and motivate us to re-experience what made us feel that way. Alcohol and other addictive substances trigger a much higher than normal increase in dopamine levels, causing an even more intense desire to repeat the behavior.
Studies have confirmed that even small amounts of alcohol cause an increase in dopamine levels. One such study, published in the journal Alcohol Health and Research World, states, This dopamine release may contribute to the rewarding effects of alcohol and may thereby play a role in promoting alcohol consumption.
You May Like: How Do You Treat Addiction
Why Are Drugs More Addictive Than Natural Rewards
For the brain, the difference between normal rewards and drug rewards can be likened to the difference between someone whispering into your ear and someone shouting into a microphone. Just as we turn down the volume on a radio that is too loud, the brain of someone who misuses drugs adjusts by producing fewer neurotransmitters in the reward circuit, or by reducing the number of receptors that can receive signals. As a result, the person’s ability to experience pleasure from naturally rewarding activities is also reduced.
This is why a person who misuses drugs eventually feels flat, without motivation, lifeless, and/or depressed, and is unable to enjoy things that were previously pleasurable. Now, the person needs to keep taking drugs to experience even a normal level of rewardwhich only makes the problem worse, like a vicious cycle. Also, the person will often need to take larger amounts of the drug to produce the familiar highan effect known as tolerance.
For more information on drugs and the brain, order NIDAs Teaching Addiction Science series or the Mind Matters series at www.drugabuse.gov/parent-teacher.html. These items and others are available to the public free of charge.
What Happens To Your Brain When You Quit Drinking
As weve noted above, an alcohol use disorder fundamentally changes the way certain key areas of the brain function. As the brain and body become more habituated to the presence of alcohol in the body, it becomes more difficult for a chronic drinker to quit drinking.
When they do decide to stop drinking, they will experience a condition known as withdrawal, as the brain resets back to its baseline functioning in the absence of alcohol. This means that the brain is no longer releasing the same levels of dopamine and other neurotransmitter chemicals that it was during chronic alcohol use. At the same time, the brain begins to restart the flow of other chemicals that were paused by alcohol.
For example, during withdrawal, the brain restarts the production of neurotransmitter chemicals that cause us feelings of stress and anxiety. While alcohol dampens the production of these neurotransmitters, they are present and active when sober. The release of these chemicals, in addition to other physical and chemical changes in the absence of alcohol, can lead an individual going through withdrawal to become more angry, depressed, frustrated, or tired than previously.
In addition to its effects on the brain, alcohol withdrawal can be life-threatening. Withdrawal often takes place within 48 hours of an individuals last drink and can lead to flu-like symptoms, including lack of energy, increased sweating, increased blood pressure and heart rate, and feelings of stress and anxiety.
Also Check: What Are Signs Of Addiction To Pain Pills
Can Neurological Complications Arise From Withdrawal
Neurological complications may result from withdrawal of certain substances. Medically supervised detox may help to reduce the likelihood or severity of many of these risks. You will receive constant monitoring and supervision as well as medication to address any symptoms or complications that may arise as a result of withdrawal.21
Withdrawal from substances like alcohol and benzodiazepines may also present a risk of withdrawal seizures.21,22 top Seizures can be dangerous because you can suffer from falls or injuries or develop a potentially lethal condition known as status epilepticus, which is when you have a seizure that lasts more than 5 minutes or when seizures occur too often in too short a time span.23
Does Alcohol Permanently Damage The Brain
Alcohol consumption, in most cases, does not cause permanent defects in reasoning, memory, or other forms of cognition. After a couple of years of sobriety, this functioning returns to normal. However, there are two main exceptions, when long-term damage can be severe and life-altering. Two of these permanent problems include Wernickeâs Korsakoff Syndrome and Hepatic Encephalopathy.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Stop Nicotine Addiction
Effects Of Alcohol On Different Populations
Alcohol affects everyone in different ways. Genes, environment and diet can influence whether a person is prone to develop an alcohol-related disease, while factors such as age, weight and sex can impact alcohols more immediate effects.
Women tend to be more vulnerable than men to the effects of alcohol due to differences in how their bodies absorb and metabolize alcohol. For women, is defined as consuming four or more drinks during a single occasion, while heavy drinking is defined as eight or more drinks per week. For men, binge drinking is defined as five or more drinks during a single occasion, while heavy drinking is 15 or more drinks per week.
The effects of alcohol addiction may also have a more serious impact on seniors, as aging changes how the body handles alcohol consumption. Alcohol abuse may worsen some health problems like diabetes, osteoporosis, memory loss, high blood pressure and mood disorders. It may also increase the likelihood of accidents such as falls and fractures.
To get help with a possible alcohol use disorder or other substance use disorder, or give us a call at .
Alcohol Impacts Your Ability To Function Normally

How immediately you feel the effects of alcohol depends on your tolerance level, what you are drinking, and how much you consume. Alcohol gets absorbed through your stomach lining and goes into your bloodstream. The brain typically starts reacting to the effects of alcohol in around ten minutes.
The physical signs that usually appear in people under the influence of alcohol include:
- Trouble walking
- Blurry vision
- Problems staying awake
Men tend to be able to consume more than women before they start feeling the effects of alcohol. As your brain continues to feel the impacts of your alcohol consumption, you may start experiencing the following feelings and emotions:
- Extreme happiness because of the release of additional dopamine
- Depression after the initial high wears off
- Disorientation as tissues in the body continue absorbing alcohol
- Excitement as the alcohol starts affecting other parts of your brain
- Loss of motor skills because the alcohol interferes with your ability to process sensory information
- Confusion as the cerebellum is affected by the alcohol
- Severe impairment of all physical, mental, and sensory abilities because of high blood alcohol levels
Read Also: How To Help My Addict Son
Different Areas Of The Brain
The brain consists of several different sections that control different aspects of what makes you human. They include:
- The Cerebral Cortex: In charge of judgment and reasoning
- The Cerebellum: Responsible for balance and coordination
- The Hypothalamus: That regulates appetite, temperature, pain, and emotions
- The Amygdala: for regulating social behavior
- The Hippocampus: the center of memory and learning
Your Brain On Alcohol
Your whole body absorbs alcohol, but it really takes its toll on the brain. Alcohol interferes with the brain’s communication pathways. It can also affect how your brain processes information.
There are several stages of alcohol intoxication:
Don’t Miss: How To Fight Video Game Addiction
Pancreas Damage And Diabetes
Normally, this organ makes insulin and other chemicals that help your intestines break down food. But alcohol jams that process up. The chemicals stay inside the pancreas. Along with toxins from alcohol, they cause inflammation in the organ, which can lead to serious damage. After years, that means you wonât be able to make the insulin you need, which can lead to diabetes. It also makes you more likely to get pancreatic cancer.
What 3 Parts Of The Brain Are Affected By Alcohol
How Alcohol Affects the Brain
- The Cerebral Cortex: In charge of judgment and reasoning.
- The Cerebellum: Responsible for balance and coordination.
- The Hypothalamus: That regulates appetite, temperature, pain, and emotions.
- The Amygdala: for regulating social behavior.
- The Hippocampus: the center of memory and learning.
Don’t Miss: What To Do If Your Child Is Addicted To Drugs
What Influences Alcohol Effects On The Brain
Numerous variables influence the impact of alcohol on the brain. The most significant factors include how much and how often the individual drinks. Other things like their overall health, genetic background, age and gender can all play a role in how they react to this substance.
A family history of alcoholism may also affect the impact of alcohol on the individuals brain, making them more vulnerable to becoming addicted to a specific substance. The amount of time theyve been drinking and the age they had their first drink also play significant roles in alcohols long-term effects on the brain.
How Alcohol Affects The Brain Brain Cells
A common expression to warn people to cut back on harmful behaviors is that they will kill their brain cells. As weve seen earlier, alcohol can fundamentally reshape and rewire the brain, but does it kill brain cells themselves? Research from Harvard Medical School found that drinking damages the brains white matter, or tissue deep inside the brain that helps us process thoughts and governs movement, as well as transmits messages between the nervous system and other regions of the brain.
While Parkinsons Disease, stroke, diabetes, and high blood pressure can also damage white matter, alcohol can speed up this cumulative damage. Researchers found that alcohol particularly damaged white matter in parts of the brain that are responsible for controlling impulses, making it less likely that individuals will be able to cut back or quit drinking.
Luckily, researchers did see one glimmer of hope, as it appeared that this damaged white matter could potentially heal if drinkers quit drinking before they reached the age of 50. While individuals who have consumed alcohol on a chronic basis for many years are at high risk of this type of damage, the risk is not limited to long-term drinkers.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Get Addicted To Kratom
