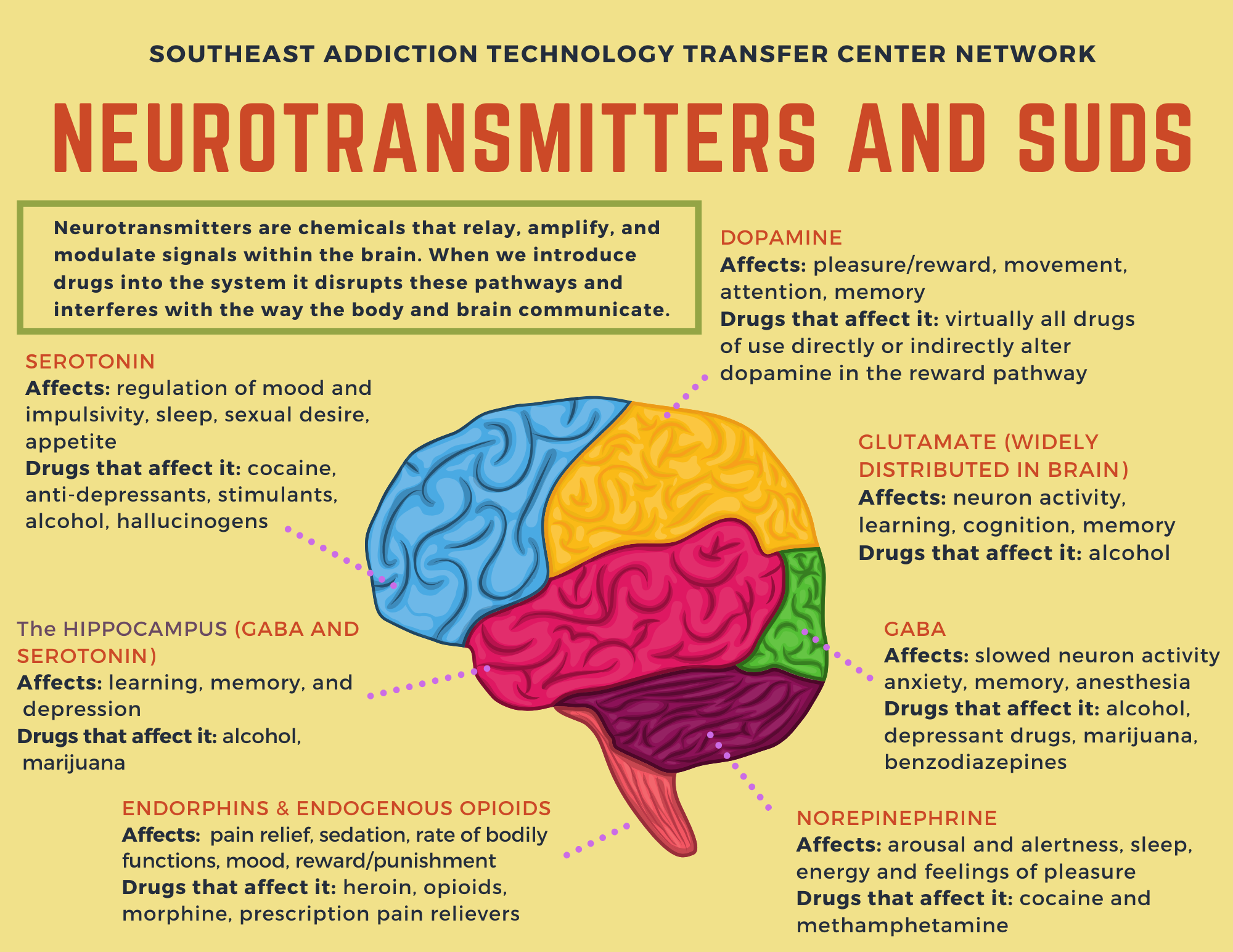
Which Neurotransmitters Are Affected
Each individual and their addiction is unique, and the same neurotransmitters may not be affected in each person. The primary neurotransmitters are serotonin, dopamine, acetylcholine, and glutamate, among others. Each of these neurotransmitters has a unique role and conveys particular messages to the brain. For example, dopamine regulates feelings of happiness, reward, and motivation. If this neurotransmitter is damaged, the individual will have difficulty feeling pleasure or reward without the crutch of drugs or alcohol.
Certain drugs affect neurotransmitters that can lessen alertness and can slow down breathing, such as heroin. In contrast, other drugs attach to the brain receptors that are responsible for dopamine regulation and feelings of euphoria, such as cocaine.
Cannabis: Neurotransmitters And Drugs
The legal name of marijuana is cannabis. The use of cannabis in any form is believed to chemically and physically change the brain. Furthermore, cannabis increases dopamine production.
The short-term effects include happiness and increased appetite. Although the effects are still being researched, long-term effects may consist of decision-making, memory, and focus issues.
Reviewhow Addictive Drugs Disrupt Presynaptic Dopamine Neurotransmission
The fundamental principle that unites addictive drugs appears to be that each enhances synaptic dopamine by means that dissociate it from normal behavioral control, so that they act to reinforce their own acquisition. This occurs via the modulation of synaptic mechanisms that can be involved in learning, including enhanced excitation or disinhibition of dopamine neuron activity, blockade of dopamine reuptake, and altering the state of the presynaptic terminal to enhance evoked over basal transmission. Amphetamines offer an exception to such modulation in that they combine multiple effects to produce nonexocytic stimulation-independent release of neurotransmitter via reverse transport independent from normal presynaptic function. Questions about the molecular actions of addictive drugs, prominently including the actions of alcohol and solvents, remain unresolved, but their ability to co-opt normal presynaptic functions helps to explain why treatment for addiction has been challenging.
- Previous article in issue
Don’t Miss: How To Not Be Addicted To Weed
Fact: Dopamine Is A Motivator
While dopamine isnt the sole cause of addiction, its motivational properties are thought to play a role in addiction.
Remember, the reward center in your brain releases dopamine in response to pleasurable experiences. This part of your brain is also closely linked to memory and motivation.
The seeds of addiction
Generally speaking, when you experience a positive sensation and dopamine is released into the pathways of the reward center, your brain takes note of:
- What triggered the sensation: Was it a substance? A behavior? A type of food?
- Any cues from your environment that can help you find it again. Did you experience it at night? What else were you doing? Were you with a certain person?
When youre exposed to those environmental cues, youll begin to feel the same drive to seek out that same pleasure. This drive can be incredibly powerful, creating an urge thats hard to control.
Keep in mind that this process doesnt always involve harmful substances or activities.
Eating good food, having sex, creating art, and a range of other things can trigger similar responses from your brains reward center.
Which Neurotransmitter Or Neurotransmitters Does The Drug Affect

A persons experiences when using a drug reflect the functional roles of the particular neurotransmitter it disrupts. Each individual neuron manufactures one or more neurotransmitters: dopamine, glutamate, serotonin, acetylcholine, and/or any of dozens of others that scientists have identified to date. Each neurotransmitter is associated with particular effects depending on its distribution among the brains various functional areas . Dopamine, for example, is highly concentrated in regions that regulate motivation and feelings of reward, and is a strong motivator for drug use. A neurotransmitters impact also depends on whether it stimulates or dampens activity of its target neurons.
Some drugs primarily affect one neurotransmitter or class of neurotransmitters. For example, prescription opioids and heroin produce effects that are similar to those produced by the neurotransmitters endorphin and enkephalin: increased analgesia, decreased alertness, and slowed respiration. Other drugs disrupt more than one type of neurotransmitter. Cocaine, for example, attaches to structures that regulate dopamine, leading to increases in dopamine activity and producing euphoria it also produces changes in norepinephrine and glutamate systems that cause stimulant effects.
Table 1 – Neurotransmitters Implicated in Drug Use and Addiction
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take To Get Addicted To Alcohol
What Happens When Alcohol Or Other Drugs Enter The Scene
For people who have a predisposition for addiction, the circuitry in the brains reward center changes. Addiction and dopamine neurotransmitters results in a reward to certain substances or stimuli. Over time and with repeated exposure, the person begins to crave more of the substance or activity that produces the positive feelings or relief from negative feelings. But the brain is just one part of the story. Addiction has many contributing factors from genetics to socioeconomic status, ones environment and any pre-existing mental health disorders. All of these elements play a role in how we respond to alterations in neurotransmitters levels.
Dangers Of Disrupting Neurotransmitters
When neurotransmitters are disrupted through drug and alcohol abuse, it can put the individual in danger. When an individual abuses drugs or alcohol, they are disrupting the natural neurotransmitter response. Due to the impairment that occurs during drug and alcohol abuse, those whose neurotransmitters are damaged cannot make sound decisions putting their well-being in danger.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Addicted To Xanax
How Addiction And Dopamine Neurotransmitters Are Related
The mechanism by which our brains reward center regulates neurotransmitters undergoes a change when we drink alcohol or take certain drugs, and this is how these chemicals can play a role in addiction. In most people, there is a temporary shift in neurotransmitter levels after we have a drink or other substance, but those levels soon shift back to normal after we metabolize it. In other people, the brains response to a change or super-charged surge of neurotransmitters brought on by alcohol or other drugs catalyzes a response from the brains reward center that says, I have to have some more of that! This same response can occur with addictive behaviors like gambling, where a person feels a rush of excitement with the anticipation of winning .
Fact: Dopamine Plays A Role In Developing Tolerance
In the context of drugs, tolerance refers to the point at which you stop feeling the effects of a drug to the same degree that you used to, even though youre consuming the same amount of the drug.
If you develop a tolerance to a substance, youll need to use more of it to feel the effects youre used to. Dopamine plays a role in this process.
Consistent drug misuse eventually leads to overstimulation in the reward center. Its pathways become overwhelmed, making it harder for it to handle the high levels of dopamine being released.
The brain tries to solve this problem in two ways:
- reducing dopamine receptors
Either change generally results in the substance having less of an effect due to a weaker response by the brains reward center.
Still, the craving to use remains. It just takes more of the drug to satisfy it.
Addiction is a complex brain disorder that doesnt have a single, obvious cause. Dopamine plays a role, but its one small piece of a larger puzzle.
Experts believe a range of biological and environmental factors can significantly increase someones risk for addiction.
Some of these biological factors include:
Environmental factors, particularly for children and teenagers, include:
These are just some of the many factors that can contribute to addiction. Keep in mind they dont mean an addiction will definitely develop.
Also Check: How To Live With An Addict
Opioid Addiction & Hpa Axis
Long-term morphine use increases pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, in turn upregulating NMDA receptors , which then reduces GABA levels . Opioids also upregulate GABAs interaction with serotonin neurons, which results in decreased serotonin activity during withdrawal, meaning that serotonin levels deplete. Withdrawal also causes hyperactivity of norepinephrine, resulting in anxiety and increased stress. This increased stress response in combination with low dopamine, serotonin, and GABA makes the withdrawal process horrible for addicted individuals. It is estimated that 3-16% of the population is genetically predisposed to addiction, but even without predisposition, the disruption in HPA-axis balance stemming from long-term opioid use is a perfect recipe for development of an addiction. Methadone is a common treatment for opioid addiction as it prevents further dopamine desensitization in the brain. Methadone is almost completely detoxified by the body and has a much longer half-life than other opioids , so its therapeutic use can be highly effective. Treatment of opioid addiction can be a painful and long process, but is exceptionally rewarding if successful. Its important to discuss detoxification programs and functional, integrative approaches to treatment with a healthcare provider.
Clinical Contributor
Ramona Richard, MS, NC
Stay up to date with sanesco
The Effects Of Drugs And Alcohol On Neurotransmitters In The Brain
The damage drug and alcohol use inflicts on the brains neurotransmitters can cause continuing deterioration, altering the neurotransmitters, causing temporary or permanent damage. But which neurotransmitters are involved in addiction, and why is it important to understand the relationship?
When consumed over an extended period, drugs and alcohol can decrease the brains ability to produce feel good chemicals naturally. Short-term exposure to alcohol releases -aminobutyric acid , a primary restraint neurotransmitter in the brain. When this is released, sedative-like effects occur. When alcohol is combined with other substances such as drugs, the results become exacerbated.
Read Also: Why Do Drug Addicts Lose Teeth
Research Into Addiction And The Brain The Role Of Neurotransmitters
The human brain under healthy conditions produces adequate amounts of dopamine, which is one of the brains feel-good chemicals. Under the influence of addiction, brain function lacks the ability to produce adequate amounts of dopamine. The theory is that this causes people to continue to seek substances and behaviors that produce more dopamine, even when the consequences of addiction begin to mount.
Interesting to note, neurotransmitters in the addict brain look normal in brain scans when under the influence of the addictive substance or behavior. For non-addicts, the inebriated brain looks abnormal. For addicts, the addiction normalizes the brain function.
This mammalian part of the brain also helps regulate emotion and is actually the emotional center of the brain. Some trauma energy is also stored here.
Together, these parts make up the primitive brain. All animals with a brain have a brainstem. All mammals have an emotional brain.
The third part is the thinking brain. Not surprisingly, this area controls thinking, decision-making and impulse control, among other functions. This is the largest part of the human brain. One key understanding related to brain function is that the connections from the thinking to the primitive brain are much less dense than from the primitive to the thinking brain. This means that emotions and traumas can affect thinking much more readily than thinking can affect emotions.
What does this mean?
The answer is most certainly, Yes!
Substance Abuse Treatments Detox & Outlook
Once the brain has become imbalanced due to drug abuse and dependence, it can take some time and effort to restore things. Cravings and emotional and physical withdrawal symptoms can be significant with some drugs, they may be dangerous or even life-threatening. The safest method to restore a chemical balance to the brain is through medical detox.
Detox is the process of allowing toxins to make their way out of the brain and body, allowing for proper healing. Medical detox is the most comprehensive form of detox. It provides 24/7 medical and mental health monitoring and supervision in a controlled and secure environment.
Different drugs may process out of the body at variable timelines, and side effects can range greatly in intensity during detox. On average, a person will remain in a medical detox program for several days to a week or two. Medications are often used to counteract withdrawal symptoms and manage drug cravings.
Withdrawal symptoms may continue beyond detox, although the acute nature of the symptoms usually begins to dissipate after this point. The brain can take more time to heal and achieve a healthy balance. NIDA recommends that an individual battling addiction remain in a treatment program for at least 90 days and longer when needed. This allows time for the brain to establish new neural connections, new habits to form, and brain chemistry to be restored.
Recommended Reading: How Much Do Addiction Counselors Make An Hour
Acute Effects Of Drugs Of Abuse On Da In The Human Brain And Its Role In Their Reinforcing Effects
To investigate the increases in DA induced by drugs of abuse and the associated reinforcing effects in humans, we chose to study cocaine since it is considered one of the most reinforcing of the drugs of abuse. Cocaine increases extracellular DA by blocking the DA transporters . We compared the acute effects of cocaine with methylphenidate , a stimulant that like cocaine increases DA by blocking DAT. These two stimulant drugs have similar affinities in vitro . However, MP has much lower levels of abuse and has well-accepted clinical use for the treatment of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder .
We used PET imaging to compare these two drugs to investigate how DA in the human brain was involved in the reinforcing effects of stimulant drugs and to determine what other variables modulated the addictive liability of this class of drugs. This work was also intended to help us understand why cocaine is much more abused than MP. The brain effects we investigated were pharmacokinetics and potency . The behavioral effects were assessed using self-report measures of high and other drug-induced experiences, which have been shown to be reliable and consistent across studies and predict self-administration of drugs in humans. The other variable we investigated was expectation effects.
Introducing The Human Brain
The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. This three-pound mass of gray and white matter sits at the center of all human activityyou need it to drive a car, to enjoy a meal, to breathe, to create an artistic masterpiece, and to enjoy everyday activities. The brain regulates your body’s basic functions, enables you to interpret and respond to everything you experience, and shapes your behavior. In short, your brain is youeverything you think and feel, and who you are.
Also Check: How Do You Become An Addiction Counselor
How Do Drugs Work In The Brain
Drugs interfere with the way neurons send, receive, and process signals via neurotransmitters. Some drugs, such as marijuana and heroin, can activate neurons because their chemical structure mimics that of a natural neurotransmitter in the body. This allows the drugs to attach onto and activate the neurons. Although these drugs mimic the brains own chemicals, they dont activate neurons in the same way as a natural neurotransmitter, and they lead to abnormal messages being sent through the network.
Other drugs, such as amphetamine or cocaine, can cause the neurons to release abnormally large amounts of natural neurotransmitters or prevent the normal recycling of these brain chemicals by interfering with transporters. This too amplifies or disrupts the normal communication between neurons.
The Role Of Neurotransmitters In Alcohol And Drug Addiction
The dopamine system has proven to play a pivotal role in the satisfying effects that alcohol induces. Alcohol affects the function of neurotransmitters in that it interacts with a number of the different neurotransmitter systems within the brain that are responsible for reward. Over time and consistent exposure to alcohol, how these neurotransmitters interact with neuronal function can eventually lead to alcoholism.
Recommended Reading: What Makes People Addicted To Drugs
Da And Vulnerability To Drug Abuse
One of the most challenging enigmas in drug addiction is why some individuals become addicted and others do not. In laboratory animals, DA function modulates the predisposition to drug self-administration and genetic manipulations of DA D2 receptors markedly affect drug self-administration. Because it is impractical to study brain DA D2 receptors levels in subjects prior to and after they become addicted, we investigated the significance that the differences in DA D2 receptor levels in nonaddicted individuals have on their responses to drugs.
This Work Has Thus Clarified The Neuronal Mechanisms That Underlie The Search For Hedonic Sensations: Contrary To What Scientists Thought Until Now These Findings Show That It Is Not Acetylcholine Alone That Regulates Dopamine Release But A Balance Between Acetylcholine And Glutamate
In order to communicate, neurons use chemical substances called neurotransmitters. Conventional neurotransmitters include dopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine and glutamate, etc.
That said, even within the group of severely dependent patients this mutation was only present in 5% of cases, indicative of the multifactorial nature of addiction and more generally the complexity of psychiatric diseases
TO CITE THIS POST :
You May Like: How To Get Certified Addiction Counselor
If Youve Wondered About Drug Addiction And The Brain Heres The Answer
More and more and more of it the addictive substance or behavior are needed to satisfy the need or craving. This is how drug addiction develops.
In short, food , television, and video games create a desire for stimulation that many children will eventually satisfy with even more harmful addictive substances and behaviors as they gain more control over what they can and cant do.
Drug addiction and the brain is no different than food or electronics. The only difference is that drugs work more quickly and the effects are more intense. Drug addiction develops for most addicts as addiction and the brain advances. The brain becomes conditioned to being over-stimulated and needs more and more to get high.
No wonder addiction seems to be cropping up everywhere in our society. We are unwittingly encouraging addiction from a very early age.
There is ongoing research related to addiction and the brain. So, new insights are happening on a regular basis. The role of neurotransmitters in addiction cant be ignored without missing the key to recovery.
Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from plentiful and simple precursors, such as amino acids, which are readily available from the diet and which require only a small number of biosynthetic steps to convert.
At RecoverYES.com, the services have been developed with a focus on addiction and the brain.
