How Does Dopamine Reinforce Drug Use
The feeling of pleasure is how a healthy brain identifies and reinforces beneficial behaviors, such as eating, socializing, and sex. Our brains are wired to increase the odds that we will repeat pleasurable activities. The neurotransmitter dopamine is central to this. Whenever the reward circuit is activated by a healthy,
pleasurable experience, a burst of dopamine signals that something important is happening that needs to be remembered. This dopamine signal causes changes in neural connectivity that make it easier to repeat the activity again and again without thinking about it, leading to the formation of habits.
Just as drugs produce intense euphoria, they also produce much larger surges of dopamine, powerfully reinforcing the connection between consumption of the drug, the resulting pleasure, and all the external cues linked to the experience. Large surges of dopamine teach the brain to seek drugs at the expense of other, healthier goals and activities.
Interferes And Changes Your Brains Chemical Signals Disrupting Regular Communication In The Brain
The brain uses a system of cells called neurons to communicate, process, and send signals. The neurons use chemical signals, called neurotransmitters, to send the messages. These messages control your thinking, decisions, and behaviors.
Many drugs interfere with this natural communication system. The drugs can prevent nerve cells from sending, receiving, or processing information as they usually would. When a person has an addiction, the substances alter the levels of neurotransmitters, which contributes to craving the drug, loss of control, and poor decision-making.
For instance, some drugs are chemically similar to natural neurotransmitters. As a result, when the drug enters the brain, it imitates the natural neurotransmitter and tricks the brains receptors to send abnormal messages.
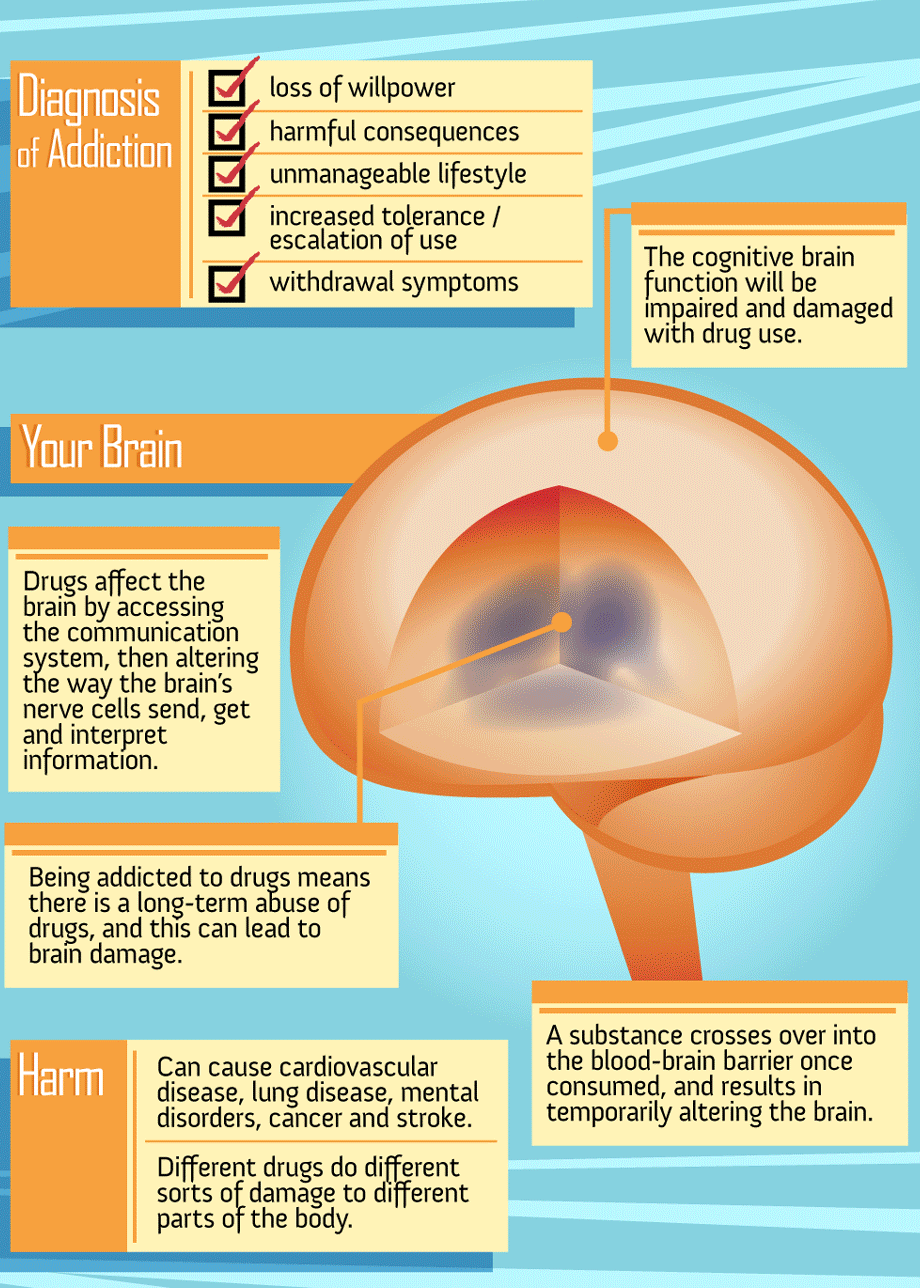
Key Points To Understand The Brain And Addiction:
1. Some characteristics of addiction are similar to other chronic diseases.
Just as cardiovascular disease damages the heart and changes its functioning, addiction changes the brain and impairs the way it works. Below is an image of the brain and the heart .
These images show how scientists can use imaging technology to measure functioning of the brain and heart. Greater activity is shown in reds and yellows, and reduced activity is shown in blues and purples. Both the healthy brain and the healthy heart show greater activity than the diseased brain and heart, because both addiction and heart disease cause changes in function. In drug addiction, the frontal cortex in particular shows less activity. This is the part of the brain associated with judgment and decision-making .
Addiction is similar to other chronic diseases in the following ways:
- It is preventable
- If untreated, it can last a lifetime
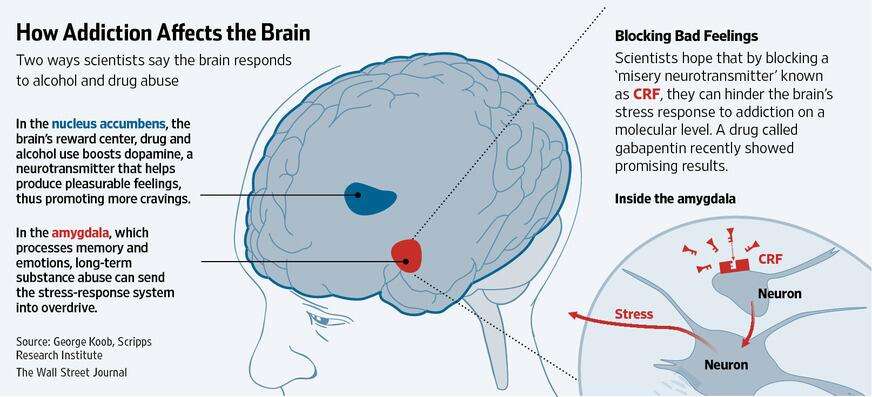
2. Substances of misuse trick the brains reward system.
Below is a picture of the brain and the nucleus accumbens, in addition to some other brain regions that are affected by addition.
The brains nucleus accumbens activated by alcohol
Addictive drugs can provide a shortcut to the brains reward system by flooding the nucleus accumbens with dopamine. Additionally, addictive drugs can release 2 to 10 times the amount of dopamine that natural rewards do, and they do it more quickly and reliably.
3. The brain can recover but it takes time!
You May Like: How To Fight Meth Addiction
Addiction Vs Abuse And Tolerance
Drug abuse is when you use legal or illegal substances in ways you shouldnt. You might take more than the regular dose of pills or use someone elses prescription. You may abuse drugs to feel good, ease stress, or avoid reality. But usually, youre able to change your unhealthy habits or stop using altogether.
Addiction is when you cant stop. Not when it puts your health in danger. Not when it causes financial, emotional, and other problems for you or your loved ones. That urge to get and use drugs can fill up every minute of the day, even if you want to quit.
Addiction also is different from physical dependence or tolerance. In cases of physical dependence, withdrawal symptoms happen when you suddenly stop a substance. Tolerance happens when a dose of a substance becomes less effective over time.
When you use opioids for pain for a long time, for example, you may develop tolerance and even physical dependence. This doesnt mean youre addicted. In general, when narcotics are used under proper medical supervision, addiction happens in only a small percentage of people.
Continued
Introducing The Human Brain
The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. This three-pound mass of gray and white matter sits at the center of all human activityyou need it to drive a car, to enjoy a meal, to breathe, to create an artistic masterpiece, and to enjoy everyday activities. The brain regulates your body’s basic functions, enables you to interpret and respond to everything you experience, and shapes your behavior. In short, your brain is youeverything you think and feel, and who you are.
Also Check: How To Deal With An Addictive Personality
How Does Substance Abuse Change Your Brain
Drug abuse spikes dopamine levels in our brain, which creates a sense of reward and pleasure. As humans, our brains our wired to learn from and adapt our behaviors to experiences of reward and pleasure. When something feels good we automatically desire to do it again to achieve the good feeling. This response drives users to take a drug again and again.
Are you or a loved one suffering from addiction?
Don’t wait, get the best treatment options today!
Harvard reports that there are actually changes in your brain which account for this effect. They write that:
Repeated exposure to an addictive substance or behavior causes nerve cells in the nucleus accumbens and the prefrontal cortex to communicate in a way that couples liking something with wanting it, in turn driving us to go after it.
What this means is that chronic drug use shapes your brain in a way which sets you up to experience cravings and drug-seeking behavior, two characteristic of addiction.
How Does Drug Addiction Affect The Brain
- InBlog
Drug addiction causes physical effects in the brain as well as psychological effects. Different types of drugs cause different reactions in the brain. The question How does drug addiction affect the brain? has been studied by scientists for decades, but some of the deepest effects are only becoming clear in recent years.
Also Check: What Does Rehab Do For Drug Addicts
Fighting Addiction With Corner Canyon Health Centers
Knowing the effects of addiction can motivate a person to quit drugs or alcohol, however, the physical changes in the brain make it very difficult for a person to stop using even if they want to. Although there is no cure for addiction, there is treatment and hope in recovery. If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction or a substance use disorder, do not be afraid to ask for help. Save a life and get help today.
At Corner Canyon, our doors are open to adult clients seeking healing and transformation to put their lives on the path of recovery. We understand the effects of addiction on the brain and body. Our residential treatment center offers a warm and welcoming home environment paired with exceptional individualized clinical care utilizing the latest in scientific advancement for treating both mental health and addiction treatment. For information on our program contact us today. We can help you get the treatment you deserve and stop the effects of addiction in your life.
Addiction Changes The Structure Of The Brain
Drugs also affect the brain by shrinking or enlarging specific parts of the organ. Research consistently shows that drugs and alcohol can decrease volume in the prefrontal cortex, which helps us plan, think, solve problems, make decisions, and exert self-control over our impulses. In contrast, addictive substances enlarge the basal ganglia, which is associated with habits, routines, learning, and emotion. When damaged, the basal ganglia can cause involuntary movements, muscle spasms, problems finding words, and tremors. Drugs and alcohol can also increase sensitivity in the amygdala, making substance users highly vulnerable to anxiety, irritability, and other distressing feelings associated with drug and alcohol withdrawal.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Sugar Addiction
Areas Of The Brain Affected By Substance Use
While alcohol and drugs affect the entire brain, some regions are more involved with SUD than others. The National Institute on Drug Abuse explains the effects of drugs on the brain in the article Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction, which focuses on the overstimulation of three key brain areas: the basal ganglia, the extended amygdala, and the pre-frontal cortex.
- The basal ganglia, associated with the brains reward system, recognizes pleasurable activities such as enjoying a good meal or having fun with friends. When overstimulated by drug use, though, it loses sensitivity to natural neurotransmitters, such as dopamine. With continued drug use, drugs become the only stimulus that activates this reward center.
- The extended amygdala is associated with negative emotions such as stress, anxiety, and irritability. These are symptoms a person experiences when a substance leaves the bloodstream. To avoid the negative symptoms of withdrawal, individuals often take more drugs, creating a feedback loop.
- The pre-frontal cortex is the area of the brain that governs decision making, logic, problem-solving, self-control, and impulse control. When this area of the brain is affected by drugs, confusion and poor decisions dominate the cognitive process.
Several drugs, including alcohol, affect the cerebellum. The cerebellum assists with muscle control and coordination, which is why people who have had too many drinks may stumble and weave when they walk.
Hypoxic Brain Damage From Overdose
Overdoses of certain substances can lead to potentially fatal neurological complications and injuries, including hypoxia, the shortage of oxygen delivery to the brain, and anoxia, meaning the total loss of oxygen that is usually due to hypoxia.17,18
Hypoxic brain injury can occur due to respiratory depression, a serious consequence of opioid overdose.19 In addition to being a particular risk with opioids , use of benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other sedatives can also lead to respiratory depression. Poly-substance use, which often involve combining substances that have depressant effects, such as opioids, sedatives, or alcohol. Combining substances in generalbut especially depressantscan have unpredictable and dangerous outcomes.19
Overdose survivors may develop a hypoxic brain injury that leads to long-lasting or even permanent damage such as short-term memory loss, stroke, mental disorientation, loss of body movement, changes in gait, incontinence, temporary leg paralysis, reduced motor skills, slowed reaction time, seizures, nerve injury, and memory impairment.20
Also Check: How To Help Someone With Video Game Addiction
What Is Brain Injury From Drug Use
Brain injury resulting from drug or alcohol use can range from minor damage to brain cells to severe physical damage such as in the case of brain hypoxia due to overdose.. Some of these consequences can be more serious and/or persistent, such as in the case of traumatic brain injury , stroke, and WernickeKorsakoff syndrome.1,2,3 Others can include potentially reversible changes such as mild brain atrophy and changes to white matter.4,5
Brain injury or other neurological complications can be a direct or indirect result of substance use. Brain hypoxia can result from an overdose of opioids, for example this is a result of opioids can significantly decrease the bodys respiratory drive. They can also occur due to poor health and nutrition, accidents, or increased risk-taking behaviors people engage in while theyre intoxicated or because they have a substance use disorder.3,6
Certain substances may have neurotoxic effects at high doses or with chronic exposure. These are substances that may cause damage or injury to brain cells. Taking these substances, especially over longer periods of time or at certain times in the human aging process, could increase your risk of suffering from substance-related brain changes or neurological issues. For example, high-dose or chronic amphetamine use may accelerate and enhance a persons age-related decline in dopaminergic function.1
What Other Factors Increase The Risk Of Addiction
- Early use. Although taking drugs at any age can lead to addiction, research shows that the earlier people begin to use drugs, the more likely they are to develop serious problems.31 This may be due to the harmful effect that drugs can have on the developing brain.32 It also may result from a mix of early social and biological risk factors, including lack of a stable home or family, exposure to physical or sexual abuse, genes, or mental illness. Still, the fact remains that early use is a strong indicator of problems ahead, including addiction.
- How the drug is taken. Smoking a drug or injecting it into a vein increases its addictive potential.33,34 Both smoked and injected drugs enter the brain within seconds, producing a powerful rush of pleasure. However, this intense high can fade within a few minutes. Scientists believe this powerful contrast drives some people to repeatedly use drugs to recapture the fleeting pleasurable state.
Also Check: How To Conquer Food Addiction
Stimulants And Lack Of Pleasure
Drugs like methamphetamine, cocaine, Adderall and ecstasy affect dopamine and dopamine receptors in the brain. Long term use can result in neurotransmitter and receptor damage, and even death.
Dopamine cell death can result in a person being unable to experience pleasure or happiness without using a stimulant drug. This often leads to severe depression, self-harming or self-destructive behaviors, and even suicidal thoughts.
How Do Substances Affect The Brain
Drugs and alcohol affect three primary areas of the brain: the brain stem, the limbic system, and the cerebral cortex. When substances enter the brain, they interfere with its normal processing and can eventually lead to dramatic changes in the neurons and brain circuits changes that can still be present even after an individual has stopped taking drugs.
What parts of the brain do drugs affect?
- Drugs affect three primary areas of the brain: the brain stem, the limbic system, and the cerebral cortex.
How do drugs affect the brain?
- When drugs enter the brain, they interfere with its normal processing and can eventually lead to changes in how well it works.
- There are at least two ways the drugs work in the brain:
- They imitate the brains natural chemical messengers
- They over-stimulate the brains reward circuit
- Normally, the reward circuit responds to feelings of pleasure by releasing the neurotransmitter dopamine. Drugs take control of this system, causing large amounts of dopamine to flood the system. This flood of dopamine is what causes the high or intense excitement and happiness linked with drug use.
You May Like: How To Fight Food Addiction
Background On Adolescent Substance Use
Substance use during adolescence has been associated with alterations in brain structure, function, and neurocognition. This review will present the current research regarding typical adolescent brain development and the subtle but significant abnormalities in indices of brain functioning associated with alcohol and drug use during this critical developmental period. Studies using neuropsychological assessment and structural and functional imaging will be discussed to help elucidate the relationship between neurocognition with alcohol and marijuana use. Additionally, methodological issues in neuroimaging and neuropsychological assessment research will be reviewed.
While several decades of research with adults have shown that chronic heavy drinking is associated with adverse consequences on the adult brain , this relationship has only recently been explored in the adolescent brain. Understanding the effects of alcohol and drug use on adolescent neurocognition is crucial, being that rates of use increase dramatically between ages 12 and 18. Epidemiological studies have shown that past month alcohol use increases from 17% to 45% between 8th and 12th grade, and illicit drug use prevalence expands from 8% to 22%. Lifetime rates indicate that 73% of youth have used alcohol and 48% have used illicit drugs by their senior year of high school . In the past year, 23% of youth meet diagnostic criteria for a substance use disorder by age 20 .
How Do Specific Types Of Drugs Affect The Brain Long
Different drugs are associated with varying long-term effects on the brain. While the changes that drive addiction are relatively universal, specific classes of drugs are associated with other unique effects on the brain.
The brain changes discussed below do not represent an exhaustive list of all changes that may occur as a result of using these drugs.
You May Like: How To Speak To An Addict
Effects Of Addiction On The Body
Beyond just the effect addiction has on the brain, when a person is addicted to drugs and alcohol the entire body is affected too. Drugs and alcoholaffect major organ function and with prolonged drug or alcohol addiction, permanent effects on vital systems and functions can lead to disability or even early death. The effects of addiction on the body can also carry over to physical changes.
Helping The Brain Recover From Addiction
Research on the brains recovery is limited and still relatively new. Less than a century ago, scientists thought the mature brain stopped developing new cells we now know the brain continues to create new cells and neural pathways. However, addiction recovery takes time, discipline, support, and patience. Before the brain can begin healing, the body must be clean of any residual substance. Detox can take several days to several weeks, depending on the substance and how long an individual has struggled with addiction.
The brain will start recovering the volume of lost grey matter within one week of the last drink with alcohol. Other areas of the brain and the white matter in the pre-frontal cortex take several months or longer to recover.
Rebuilding the neural pathways to reinforce healthier choices and habits depends on each individuals circumstances. Opioids and cocaine are highly addictive, which makes them more challenging to re-configure deeply ingrained neural circuits. Additionally, the longer a substance is abused, the more solidified the neural pathway for that behavior becomes.
Most drugs change dopamine levels. Many variables determine whether or not the brains capacity to release and re-uptake dopamine will ever fully recover. In addition to the specific substance and length of use, dopamine recovery depends on a persons age, genetics, mental health, and how many drugs were used simultaneously.
Categories
Contact Us
You May Like: How To Kick Alcohol Addiction
