The Dopamine Pathway Is Not The Yellow Brick Road
Neuroscientists believe that their research is at last going to enable serious progress on this ancient human affliction. The common pathway was a benchmark revelation, in part because it offered a unified framework for studying what for a long time had seemed like a hodgepodge of unrelated behaviors.
Important though it may be for understanding addiction, the dopamine pathway itself does not seem likely to yield promising new medications or other treatments for addiction. The pathway is so essential to normal functioning, to the everyday pleasures of life, and perhaps to learning itself, that it may be nearly impossible to interfere with it successfully. Whatever you do to the dopamine system, you always get more than you bargained for, Caron observes. That’s because of lack of selectivity and our lack of fundamental understanding of which protein of the dopamine system really mediates the addictive behavior.
And although genes seem more and more likely to play a key role in addiction, identifying these genes will not necessarily lead to treatments either. There’s not going to be a single gene that’s defective in people that have more liability to become addicted. You probably can have many, many changes in the brain that will all eventually manifest themselves in addictive personalities, Caron says.
What Is Neuroplasticity And What Role Does It Play In Addiction
Neuroplasticity is the brains natural ability to change its wiring patterns in response to life experience. When stimulated, nerve cells generate new tendrils of connection to other nerve cells, called synapses. All learning hinges on the brains capacity to form new nerve cell connections, and mental and behavioral flexibility is the hallmark of that capacity.
While neuroplasticity is the great liberator of the mind, allows people to learn languages and remember birthdays, and fuels the imagination, it has a dark side. The same process rewires the brain in response to using drugs of abusebut, under the influence of the unnaturally fast and large flood of dopamine released, the rewiring strengthens the desire for the drug, weakens judgment and control, and prunes away the capacity to be interested in other, more natural rewards. The capacity for neuroplasticity, however, also enables the brain to rewire itself more normally once drug usage is stopped.
The Causes Of Addiction Genetic Learned Or Both
Some people only have to smoke, inject, or ingest drugs once or twice and they find themselves addicted to the substance. Others may use drugs recreationally on and off throughout their life and never struggle with quitting. So what causes a person to be an addict of drugs or alcohol, unable to say no or stop whenever they want? It turns out that there are many factors that determine whether or not you are facing a problem with addiction.
Don’t Miss: How To Beat Marijuana Addiction
Public Enemy #: Stress
Remember we said before that the roots of CRAVING are in an over-abundance of dopamine and a deficiency of serotonin? There is one universally common factor in an imbalance between serotonin and dopamine: STRESS. Especially chronic, inescapable stress which lowers serotonin. When serotonin is low, not only do cravings increase, but depression and anxiety can also result.
In this way, a person can become vulnerable to any substitute that influences dopamine and serotonin levels, such as alcohol, drugs, or addictive processes such as sex, gambling or overeating. Ruden cites the case of Alston, now addicted to marijuana and alcohol, whose brain was forced to deal with chronic stress from a young age, a result of neglect and the low self-esteem created by his father.
His marijuana addiction plays a vital role in superficially helping him to not only regulate his emotions something he was never safely helped to do in his primary years but to satisfy his cravings for the happy, satisfied feelings produced by serotonin.
Does Your Brain Damage Heal After Quitting Drugs
Oct 6, 2021 | Blog
Drug use can interfere with the normal chemistry in the brain, and misusing medications often causes a significant amount of damage. These changes may not cause any symptoms at first, but over time they become more noticeable to both others and the user. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, drug addiction occurs when repeated drug use leads to changes in the function of multiple brain circuits. The good news is that once an individual quits taking drugs, the brain can begin to heal and over time resume its normal operation.
Also Check: Can You Get Ssi For Drug Addiction
Fighting Addiction With Corner Canyon Health Centers
Knowing the effects of addiction can motivate a person to quit drugs or alcohol, however, the physical changes in the brain make it very difficult for a person to stop using even if they want to. Although there is no cure for addiction, there is treatment and hope in recovery. If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction or a substance use disorder, do not be afraid to ask for help. Save a life and get help today.
At Corner Canyon, our doors are open to adult clients seeking healing and transformation to put their lives on the path of recovery. We understand the effects of addiction on the brain and body. Our residential treatment center offers a warm and welcoming home environment paired with exceptional individualized clinical care utilizing the latest in scientific advancement for treating both mental health and addiction treatment. For information on our program contact us today. We can help you get the treatment you deserve and stop the effects of addiction in your life.
Addiction Is The Result Of Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity isthe ability of your brain to change its physical structure and function based on life experiences and repeated behaviors, emotions, and thoughts. Because of neuroplasticity, what you do habitually both good and bad literally gets wired into the structure of your brain.
Neuroplasticity is the basis for all learning and makes the brain amazingly resilient. It has enabled people to recover from injuries and birth abnormalities, improve neurological deficits, pull out of psychological conditions and reverse behavioral patterns. However, this same characteristic makes the brain very vulnerable as well. Its because of neuroplasticity that addictions become ingrained in your brain, valuable skills are lost as your brain ages, and some brain illnesses and conditions show up in humans.
Read Also: Is My Kid Addicted To Video Games
Definitions Of Key Terms
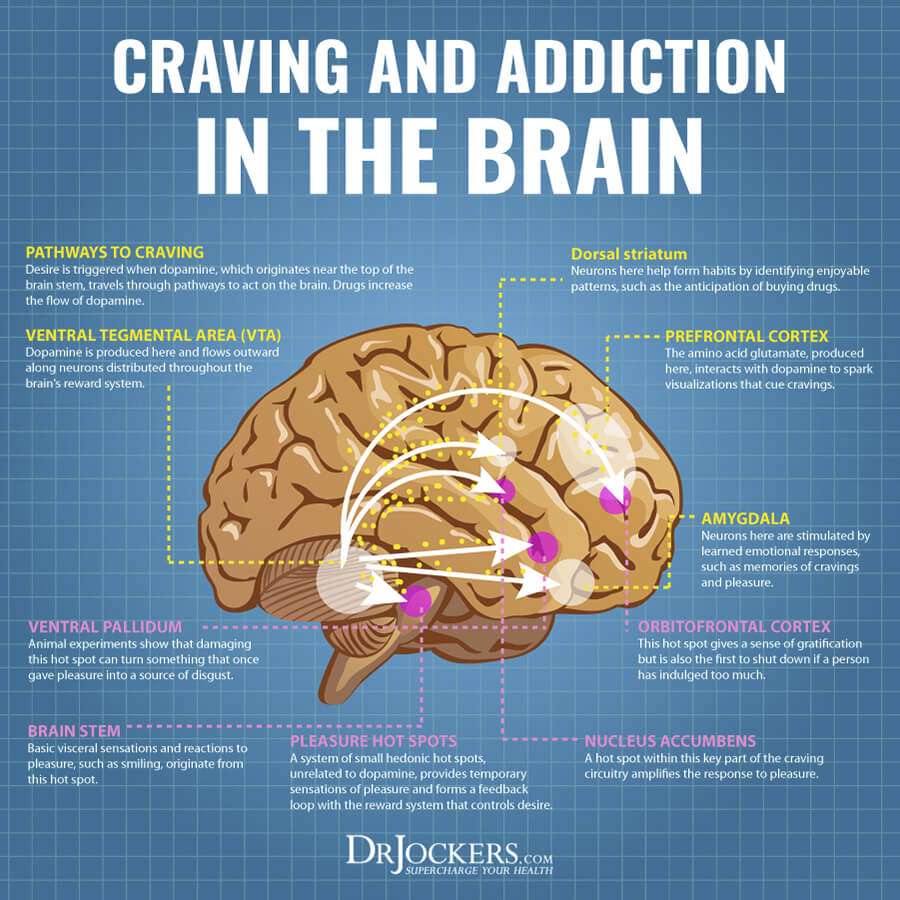
dopamine : A neurotransmitter present in brain regions that regulate movement, emotion, motivation, and the feeling of pleasure.
GABA : A neurotransmitter in the brain whose primary function is to inhibit the firing of neurons.
locus ceruleus : A region of the brain that receives and processes sensory signals from all areas of the body involved in arousal and vigilance.
noradrenaline : A neurotransmitter produced in the brain and peripheral nervous system involved in arousal and regulation of blood pressure, sleep, and mood also called norepinephrine.
nucleus accumbens : A structure in the forebrain that plays an important part in dopamine release and stimulant action one of the brains key pleasure centers.
prefrontal cortex : The frontmost part of the brain involved in higher cognitive functions, including foresight and planning.
ventral tegmental area : The group of dopamine-containing neurons that make up a key part of the brain reward system key targets of these neurons include the nucleus accumbens and the prefrontal cortex
What Parts Of The Brain Are Affected By Drug Use
Drugs can alter important brain areas that are necessary for life-sustaining functions and can drive the compulsive drug use that marks addiction. Brain areas affected by drug use include:
Some drugs like opioids also disrupt other parts of the brain, such as the brain stem, which controls basic functions critical to life, including heart rate, breathing, and sleeping. This interference explains why overdoses can cause depressed breathing and death.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take To Be Addicted To Heroin
Looking For A Place To Start
Reach out to a treatment provider for free today.
- About
Krystina Murray has received a B.A. in English at Georgia State University, has over 5 years of professional writing and editing experience, and over 15 years of overall writing experience. She enjoys traveling, fitness, crafting, and spreading awareness of addiction recovery to help people transform their lives.
- LiveScience.com. Pappas, Stephanie. . This Is Your Brain On Drugs . Retrieved On June 18, 2019 at
- LiveScience.com. Saplakoglu, Yasemin. . How Drug Addiction Hijacks The Brian. Retrieved On June 18, 2019 at
- Neuroceters.com. . Neuroceters.com. . Whats The Difference Between Biofeedback And Neurofeedback? Retrieved On June 18, 2019 at
- NCIB.com. Dimeff, Linda. Linehan, Marsha. . Dialectical Behavior Therapy For Substance Abuse. Retrieved On June 18, 2019 at
- NCIB.com. Gray, Sarah. . An Overview of The Use Of Neurofeedback Biofeedback For The Treatment Of Symptoms Of Traumatic Brain Injury In Military And Civilian Populations. Retrieved On June 18, 2019 at
Clinically Reviewed:
David Hampton
- About
Genes And Substance Abuse
Heredity
is the process of parents passing on traits to their children at birth.4 Children receive 46 chromosomes containing thousands of genes from their parents. Genes determine the specific traits that a child will have, such as:5
- Physical traits: determine a persons outer appearance, such as eye and hair color.
- Behavioral traits: influence the way a person acts, such as how shy or outgoing a person is.
- Predisposition to medical conditions: can also be impacted by traits and may increase a persons risk of getting a disease, such as cancer.
Although genes play a role in defining a persons traits, environmental factors can also impact traits.5 Environmental influences can even alter a trait.5
Addiction is considered moderately to highly heritable, meaning that genetics play a significant role in addiction.6 In other words, people who have relatives with addiction problems have an increased risk of developing an addiction themselves.
The influence of genetics on addiction varies from drug to drug. Below is the breakdown of heritability of dependence on or abuse of specific drugs.6
- Cocaine: .72 heritability or 72%
- Opiates: .70 heritability or 70%
- Alcohol: .55 heritability or 55%
- Sedatives: .50 heritability or 50%
- Hallucinogens: .39 heritability of 39%
Specific genes that have been linked to addiction include:7
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Fast Food Addiction
The Role Of Personal History
Further evidence to refute the theory of drug-induced addiction is depicted in heroin use during the Vietnam War, when many American soldiers were routinely using heroin. Ten months after returning home, only 5% of those solders considered addicted were still using. This is an excellent recovery rate, not accounted for by treatment.
It begged the question: Is a substance intrinsically addicting, or do other life experiences determine compulsive use? .
Findings of the Adverse Childhood Experiences study demonstrate that unrecognized adverse childhood experiences are a major factor underlying addiction. These adverse childhood experiences result in neurodevelopmental changes and emotional damage . These experiences can predispose one to negative emotional states and create a strong motivation for seeking reliefthrough psychoactive substance use which provides short-term benefit in the face of long-term risks.
Addiction Is Not A Moral Failure Its A Brain Disorder

For many years now, a social stigma has existed around addiction, whether to alcohol, illicit drugs, food or something else. The seriousness of these disorders has been widely viewed as the result of poor self-control and personal behavioral choices.
This perspective was hard for Dr. Nora Volkow to comprehend when her addicted patients told her that even though the drug they were taking was no longer pleasurable, they couldnt stop taking it. Were people really willing to give up everything they cared for family, friends, health and freedom for something they perceived as rewarding due to their moral failures, or was a physiological disorder causing their addiction?
In this TEDMED talk, Dr. Volkow discusses how images of the human brain are providing insight into the role that the chemical dopamine plays in addiction.
Dopamine is the chemical in the brain that tell us something is rewarding or pleasurable, and it enables us to take action. For addicted individuals, simply seeing, hearing or smelling the reward in this case alcohol, drugs or even food produces sharp, short-lasting increases in dopamine. Dopamine D2 Receptors regulate the frontal lobe of our brain which gives us the ability to control strong urges and exhibit self-control. Repeated and frequent substance abuse leads to a reduction of these receptors, compromising our ability to control strong urges.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Being Addicted To Food
Coffee And Donuts Soda And Candy Recipe For Failure
So, someone goes into treatment or a 12-Step meeting desperate and committed to sobriety. They enter with depleted neurotransmitters and a starving brain. Often they are in withdrawal, craving, foggy, depressed and anxious at best. They are told they need pharmaceutical drugs to deal with their symptoms.
Sometimes candy are encouraged to stop the craving. Many addicts then switch their addiction to sugar, which should be classified as a potent addictive drug. The desperate addict gains too much weight and stays moody.
There are treatment programs residents are fed healthy food and feel better. They often return to their former unhealthy eating habits when they leave, however. No one taught them how to shop or cook for themselves.
They know to avoid hunger but not what to feed their brains and how vital it is to avoid SUGAR. They have been given zero instruction on the nutrition supplements so essential to healing their broken brain chemistry. Is it any wonder the relapse rate is so high?
The Implications For Treatment
Traditionally, people with addictions have sought and received treatment for a particular substance or behavior. This has sometimes resulted in the person substituting one addiction for anotherwhat ASAM calls the “pathological pursuit of rewards”because the underlying cause was not treated.
ASAM suggests that comprehensive addiction treatment should focus on all active and potential substances and behaviors that could be addictive. ASAM was careful to point out that the fact that addiction is a primary, chronic brain disease does not absolve addicts from taking responsibility for their behaviors.
Just as people with heart disease or diabetes have to take personal responsibility for managing their illness, if you have an addiction, you also must take the steps necessary to minimize your chance of relapse, ASAM said.
If you or a loved one are struggling with substance use or addiction, contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357 for information on support and treatment facilities in your area.
For more mental health resources, see our National Helpline Database.
Also Check: How To Counsel Drug Addicts And Alcoholics
If A Family Member Was Addicted Will I Become Addicted
The vast majority of children whose parents abuse alcohol or drugs do not grow up to do the same. However, they are at some increased risk for doing so, and there are a number of reasons why. For one, they are exposed to those substances, and exposure during early adolescence may especially influence substance use.
For another, they may inherit whatever genetic or biological vulnerabilities laid the groundwork for a parental addiction. But they may also be more prone to addiction because they suffer from cognitive, emotional, or behavioral problems known to arise in children as a consequence of growing up in a home marked by substance use for example, as children they are at increased risk of neglect, abuse, or a poor quality parent-child relationship.
What Does Addiction Do To The Brain
Addiction impacts the brain on many levels. The chemical compounds in Stimulants, Nicotine, Opioids, alcohol, and Sedatives enter the brain and bloodstream upon use. Once a chemical enters the brain, it can cause people to lose control of their impulses or crave a harmful substance.
When someone develops an addiction, the brain craves the reward of the substance. This is due to the intense stimulation of the brains reward system. In response, many users continue use of the substance this can lead to a host of euphoric feelings and strange behavioral traits. Long-term addiction can have severe outcomes, such as brain damage, and can even result in death.
Scroll to Find Your Insurance
Addiction Center is not affiliated with any insurance.
Don’t Miss: Who Is An Addict Na
The Good News For Addicts
Even if youve become addicted to drugs and they have altered your brains functioning and structure, drug rehabilitation can help. Through therapy, detox, medication, and a switch to a healthy lifestyle, you can reverse the disease. And you dont need to hit rock bottom before receiving help. The sooner you admit to yourself that you have a problem, the better. Contact us today at Vertava Health to get started.
Box 1 Whats In A Name Differentiating Hazardous Use Substance Use Disorder And Addiction
Although our principal focus is on the brain disease model of addiction, the definition of addiction itself is a source of ambiguity. Here, we provide a perspective on the major forms of terminology in the field.
Hazardous Substance Use
Hazardous substance use refers to quantitative levels of consumption that increase an individuals risk for adverse health consequences. In practice, this pertains to alcohol use . Clinically, alcohol consumption that exceeds guidelines for moderate drinking has been used to prompt brief interventions or referral for specialist care . More recently, a reduction in these quantitative levels has been validated as treatment endpoints .
Substance Use Disorder
SUD refers to the DSM-5 diagnosis category that encompasses significant impairment or distress resulting from specific categories of psychoactive drug use. The diagnosis of SUD is operationalized as 2 or more of 11 symptoms over the past year. As a result, the diagnosis is heterogenous, with more than 1100 symptom permutations possible. The diagnosis in DSM-5 is the result of combining two diagnoses from the DSM-IV, abuse and dependence, which proved to be less valid than a single dimensional approach . Critically, SUD includes three levels of severity: mild , moderate , and severe . The International Classification of Diseases system retains two diagnoses, harmful use and substance dependence .
Addiction
Integration
Don’t Miss: What Is An Addictive Personality
