Physical Effects Of Addiction
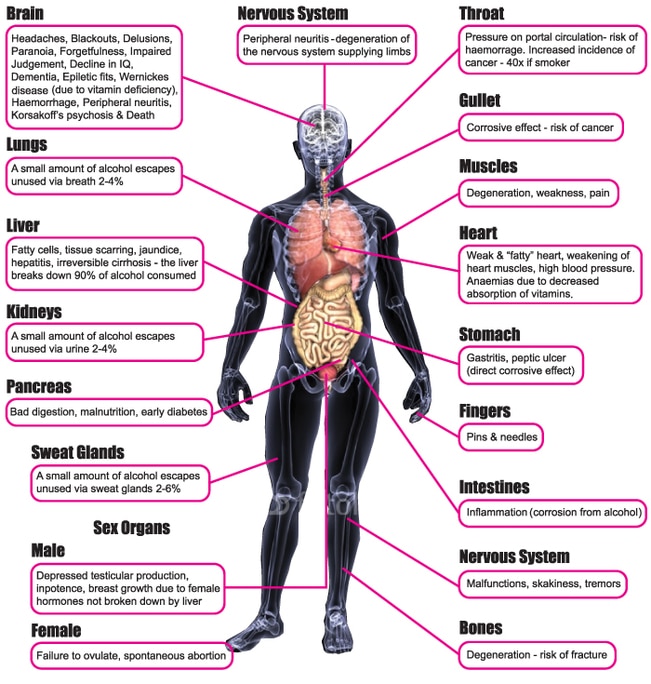
While many of the primary effects of addiction occur in the brain, the rest of the body can suffer as well. Substance abuse weakens the immune system and leaves the body more vulnerable to various diseases and infections. Drug useespecially through needlesincreases an individuals chance of contracting HIV, hepatitis, or other infectious diseases. Other physical effects of addiction include abdominal pain, digestive issues, trouble sleeping, or even seizures and other forms of brain damage. Addictive substances can impact every part of the body even beyond the following common issues.
Effect Of Alcohol On Weight Loss
In addition to causing health problems with ones organs, heavy alcohol consumption also causes people to gain weight. Alcohol often contains calories that lead to increased weight gain. Alcohol also contains primarily empty calories, causing the body to have to focus on metabolizing the calories present in alcohol instead of other calories that would lead to weight loss.
Causes And Risk Factors For Addiction
It can be hard to ascertain why one individual becomes addicted to a drug while another does not. Researchers believe that addiction is not based upon one single cause, but rather a number of factors working together. Most common causes for substance abuse include:
Genetic: While unclear which genes are responsible, it is known that addiction has a genetic component. Individuals who have a family history of addiction especially by a close relative are more likely to develop an addiction themselves.
Brain Chemistry: Researchers believe that some individuals may be born lacking proper amounts of neurotransmitters responsible for pleasure. In response to this inborn deficiency, some individuals may turn to drugs to induce feelings of pleasure.
Environmental: Individuals born into homes in which addiction runs rampant are more likely to grow to develop a substance abuse disorder. Additionally, those who begin to abuse substances at an early age are more likely to develop an addiction later in life.
Psychological: Many individuals struggle with under treated or undiagnosed mental illnesses. These people may turn to substance abuse as a means to self-medicate the symptoms of their mental illness.
Signs and Symptoms
You May Like: Substance Use Disorders And Addictions
What Do Drugs Really Do Your Body
Every time you drink a beer, you smoke a joint, you pop a pill, you take a hit you make a choice. You make an active choice to put substances in your body because, in the heat of the moment, it seems like the right thing to do. It will make you feel better, it will get you high, it will be fun. This is what you tell yourself. But did you know that it is also putting your health in danger?
We know youve heard it before. Your parents told you that drugs are bad. Your friends told you to stop drinking so much. Maybe a doctor has even said that your drug use has taken a toll. Not to mention, you know hangovers and come-downs quite well. Unfortunately, drug addiction is a persistent thing. It is your brain relentlessly telling you that its okay to take drugs, despite the physical consequences and the terrible aching your body experiences soon after. And it makes you wonder, what do drugs do to your body, exactly? Why do you feel this way, and why cant you stop? What are the risks if you keep using?
Effects Of Drug Addiction On The Brain
All drugsnicotine, cocaine, marijuana and othersaffect the brains reward circuit, which is part of the limbic system. This area of the brain affects instinct and mood. Drugs target this system, which causes large amounts of dopaminea brain chemical that helps regulate emotions and feelings of pleasureto flood the brain. This flood of dopamine is what causes a high. Its one of the main causes of drug addiction.
Although initial drug use may be voluntary, drugs can alter brain chemistry. This can actually change how the brain performs and interfere with a persons ability to make choices. It can lead to intense cravings and compulsive drug use. Over time, this behavior can turn into a substance dependency or drug and alcohol addiction.
Alcohol can have short- and long-term effects on the brain and disrupts the brains communication pathways. These can influence mood, behavior and other cognitive function.
Brain damage may also occur through alcohol-induced nutrition deficiencies, alcohol-induced seizures and liver disease. In pregnant women, alcohol exposure can impact the brains of unborn babies, resulting in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.
It is reported that alcohol-induced brain problems can often be corrected with proper treatment. Abstinence from alcohol for months or years can help partially repair thinking abilities, like memory skills.
You May Like: Is Alcohol The Most Addictive Drug
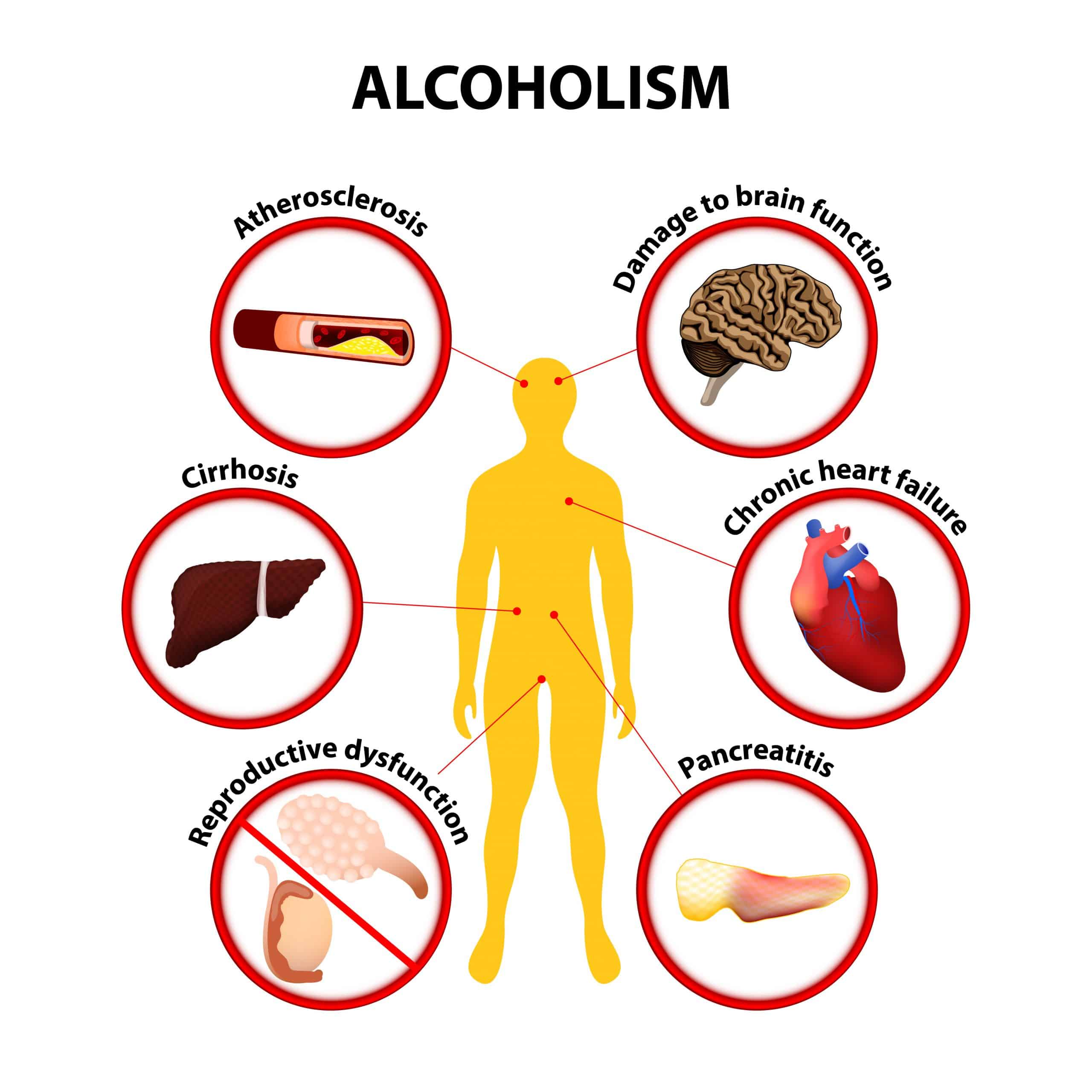
Psychological And Physical Effects Of Addiction
Addictive substances have a way of taking over someones life. Chronic or repeated use of drugs or alcohol can create short-term and long-term negative effects on the body and mind. These substances can damage the organs and alter the brain, leading to mental health disorders, organ damage or failure, and other health complications. Its not just the addicted individual who suffers either. Friends and family members all experience the consequences of drug or alcohol addiction. As with many problems, knowledge and information can make it easier to identify and confront the issues surrounding addiction. To help you learn more, here is our overview of the psychological and physical effects of addiction.
How Is Substance Use Disorder Diagnosed
A single test cant diagnose substance use disorder. Instead, healthcare providers rely on a thorough evaluation of your medical history and behaviors surrounding substance use. They may order drug tests and evaluate prescription drug monitoring program reports.
A provider will also ask about your mental health history, as its common to have an SUD and a mental health condition.
According to the American Psychiatric Associations Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , a person must have at least two signs in the symptoms section over 12 months to be diagnosed with substance use disorder.
Its important to remember that SUD exists on a spectrum of severity:
- Two to three signs indicate a mild substance use disorder.
- Four or five signs indicate a moderate substance use disorder.
- Six or more symptoms indicate a severe substance use disorder.
You May Like: 12 Core Function Of Addiction Counseling
Ways How Drugs Affect A Human Body Physically
If we talk about how drugs affect a human body than there is no short answer to this, drug addiction is all about killing a human body slowly and sometimes fast. We donât understand the damages initially but later when it starts becoming a disease we understand the physical damages and it affects. 10 ways how drugs affect a humanbody physically are as follow:
Cocaine & The Cardiovascular System
Much research has been conducted into what cocaine abuse does to the heart and cardiovascular systems in the long-term. The American Heart Association noted that cocaine users had an abnormal flow of blood into the hearts vessels, which can cause serious heart problems or even death. Unfortunately, much of this damage is not immediately detectable, so users might consume cocaine for prolonged periods of time before feeling something significantly wrong. The hearts vessels become overdilated as a result of the cocaine abuse, which makes them pump blood much faster than normal, and this causes the usual chest pain and shortness of breath. Cocaine also raises blood pressure levels, since the heart has to work harder. Over time, the walls of blood vessels become weaker, and the heart muscle itself can become damaged from the frenzy, leading to aneurysms, heart attacks, and death.
The journal of Circulation notes other long-term effects of cocaine abuse on the heart and cardiovascular systems in the long-term, such as myocardial infarctions, cardiomyopathies, endocarditis, and aortic dissection. Taking cocaine for a period of time may also exacerbate pre-existing heart conditions, hastening the damage to the heart and causing lasting problems with breathing, circulation, and blood pressure.
Also Check: How To Be Supportive To An Addict
Hair & Skin Issues Related To Stress
Stress can cause physical changes to the skin, leading to skin issues and conditions such as acne, psoriasis, and acne. The stress response can make your skin more sensitive and reactive, creating these potential issues and making it harder for your skin to heal.
Your skin produces more oil during times of stress, which can lead to breakouts. Permanent hair loss is also related to chronic stress.
Stress changes the brain and body chemistry. Over time, this can have outwardly detrimental effects on the body, which can be seen in skin and hair changes.
How Do Drugs Affect The Body
Drugs change the way your body works. Even seemingly quiet drugs like marijuana and prescription Adderall can have a detrimental effect. The truth is, any addictive drug, in any dosage, used for a prolonged period of time, can cause major damage to your physical health.
When you abuse drugs, you run the risk of respiratory depression, heart attack, coma, overdose, stroke, hypothermia, dehydration, blood disorders, gastric problems, panic attacks, and cognitive deficits. The list goes on. Drug use can make you look and feel weak, malnourished, and can destroy your immune system over time. Studies show that individuals who do not seek treatment for their drug problems only have a life expectancy of 15 to 20 years after the onset of their drug addiction. This means that if you started using drugs at 18-years-old, and have continued to do so without professional drug treatment, your life expectancy will not exceed age 40.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Recover From Opiate Addiction
Finding Treatment For Alcoholism
Alcohol use disorders, or alcoholism, occur on a spectrum, and each person is unique. If you or someone you know is ready to discuss treatment, our admissions navigators are available 24/7 to speak with you today at . The type of treatment that will be most suitable for you will likely be influenced by your alcohol history, other substance use history, previous attempts at treatment, any co-occurring medical and/or mental health conditions, and your current situation.
For further information on treatment during the pandemic, weve put together a guide that answers some of our most frequently asked questions:
As the leader in addiction treatment American Addiction Centers specializes in helping people recover from alcohol addiction. If you are looking for more information about alcohol addiction, find some useful information for those seeking guidance or you can learn more about insurance coverage and instantly verify insurance with an AAC facility:
What Is The Treatment For Substance Use Disorder
Effective treatments are available for substance use disorder. Treatment is highly individualized one person may need different types of treatment at different times.
Treatment for SUD often requires continuing care to be effective, as SUD is a chronic condition with the potential for both recovery and relapse.
As people with SUD often have co-occurring mental health conditions, treating them together rather than separately is generally better.
The three main forms of treatment include:
- Detoxification.
- Long-term therapeutic communities, such as sober living communities.
Detoxification
In detoxification, you stop taking the substance, allowing them to leave your body. Depending on the severity of the SUD, the substance or an alternative may be tapered off to lessen the effects of withdrawal. Its the first major step of treatment for SUD. You can go through detoxification in both inpatient and outpatient settings.
Cognitive and behavioral therapies
Psychotherapy can help treat SUD and any other co-occurring mental health conditions. Therapy also teaches healthy coping mechanisms.
Healthcare providers may recommend cognitive and behavioral therapies alone or in combination with medications.
Some examples of effective therapies for adults with SUDs include the following:
Participating in self-help programs, like Narcotics Anonymous, can also play a significant role in SUD treatment.
Medication
Medication-assisted treatments are available for:
Also Check: How To Stop Being Addicted To Technology
Alcohol And Immune System
Alcohol is known to suppress the normal function of your immune system. When used excessively, alcohol affects the immune system in many different ways. The exact mechanisms by which alcohol suppresses the immune system are not fully understood however, the research is clear that heavy alcohol use increases the risk of infections such as pneumonia, sepsis and poor wound healing. The immune system plays an important role in fighting cancer, and the effects of alcohol on the immune system may be part of what makes alcohol increase the risk of developing cancer.
The Immune System & Stress
When you are stressed, the immune system is activated as part of the fight-or-flight response. This can help to ward off infections and heal injuries.
When your body is in a chronic state of stress, however, the constant influx of stress hormones can actually weaken the immune system. This can leave you more vulnerable to infections and viral illnesses, such as the flu or a common cold. It can also take your body longer to heal from injury or illness when it is under chronic stress.
You May Like: How Many People Are Addicted To Porn
Whos Most Likely To Become Addicted
Each personâs body and brain are different. People also react differently to drugs. Some love the feeling the first time they try it and want more. Others hate it and never try again.
Not everyone who uses drugs becomes addicted. But it can happen to anyone and at any age. Some things may raise your chances of addiction, including:
- Family history. Your genes are responsible for about half of your odds. If your parents or siblings have problems with alcohol or drugs, youâre more likely as well. Women and men are equally likely to become addicted.
- Early drug use. Childrenâs brains are still growing, and drug use can change that. So taking drugs at an early age may make you more likely to get addicted when you get older.
- Mental disorders. If youâre depressed, have trouble paying attention, or worry constantly, you have a higher chance of addiction. You may turn to drugs as a way to try to feel better. A history of trauma in your life also makes you more likely to have addiction.
- Troubled relationships. If you grew up with family troubles and arenât close to your parents or siblings, it may raise your chances of addiction.
Also Check: How Many Addictions Are There
Thinking Patterns Are Reordered
Scientists are always at odds when it comes to the nature vs. nurture debate. While the nature side of the argument points out that certain things about us are inherent and unchangeable since birth, nurture proponents emphasize the fact that how we behave, and what we are exposed to, work to create our experience of being human.
Most of us are able to discern that, when it comes to patterns of thinking, we have added quite a bit to the thinking process which we utilized as a child. Our thought patterns are able to adapt and grow as we go through life, and hopefully with the outcome of our being able to reason more effectively. While under the constant influence of an addictive substance, however, our evolution of thinking is often stunted. The concept of Parallel Distributed Processing explains this stunting of thought development from a biological perspective.
In simple terms, PDP can be compared to how a stream of water turns into a river. When the stream is small, it is easily diverted. We can change the course of this stream by kicking some dirt into the path, or through digging some gullies with a shovel. As the stream of water grows more powerful, it will begin to cut out its own pathways through the ground. Eventually, as the stream turns into a river, its course becomes set, and we can predict exactly how it will flow.
You May Like: How Many Times Does An Addict Relapse
Effects Of Drug Addiction
The definition of drug addiction refers to the obsessive and repeated use of dangerous amounts of drugs and the appearance of withdrawal symptoms when not using drugs. The effects of drug addiction seen, due to this compulsion, are wide-ranging and profound. Effects of drug addiction are felt by the addict both physically and psychologically. The effects are also seen in those around the addict, like family members.
The effects of drug addiction also include the cost to the justice and health care systems. Violent behavior is most closely tied to alcohol use and alcohol abuse is responsible for the disability of 58.3 million people worldwide.1 It was estimated the effects of drug addiction cost the U.S. $245.7 billion in 1992. This number represents health care expenses, lost wages, prevention program costs and criminal justice system costs, among others.2
The Risks Of Overdose
The most serious potential long-term effect of drug abuse and drug addiction is death. Drugs can kill slowly over time, but they can also cause a fatal overdose. Any misuse of any type of drug puts a person at risk for having an overdose that may be fatal. That risk increases when using street drugs, because the strength or purity is impossible to know. The risk also increases when combining drugs or using drugs with alcohol. For example, combining substances that depress breathing, like opioids and sedatives, greatly increases the risk of a fatal overdose.
Drug abuse and drug addiction have serious and lasting impacts on all aspects of a personâs health, as well as other areas of life, like relationships and finances. But anyone who abuses drugs has reason to hope in spite of these effects. Good, effective, long-term treatment can help reverse much of the damage caused by drugs and gives a person a chance to put their life back together.
Read Also: How To Stop Weed Addiction
What Does Addiction Do To The Brain And Body
The effects that drugs and alcohol have, to the point of addiction, cause four key changes in the brain. What happens in the brain also impacts the body, from its stability to functionality. The difficulty is that the brain is highly adaptive, which will accommodate such changes, making it very easy for a tolerance to develop and an addiction to materialise.
Firstly, consumption to addictive levels can disrupt the limbic system. The limbic system controls our emotional responses. Its also the part of the brain which filters out pleasure and taught behaviours. Drugs and alcohol are favoured for the pleasure that they offer. Not only will their effects increase cravings and the likelihood of repeat actions but will also affect brain chemistry and structures.
Secondly, the cerebral cortex which carries information through our bodies and also controls our key senses can be disturbed through addiction. Heavy consumption can impact functionality, disrupt the flow of information, and heighten senses.
Thirdly, homeostasis is the bodys natural balance, making sure that all internal systems are stable and healthy. Addiction can adjust the brains natural balance through highly stimulating and unstable habits. Adjustments can negatively impact homeostasis, found to cause obsessive behaviours, chronic cravings, and high urges to repeat behaviours.
