Five Reasons Spice Is A Dangerous Last Resort Drug
Spice is one of the newer drug is in town and its wreaking havoc among the homeless, military personnel, students, prisoners and those on probation or parole. This designer drug mimics marijuana , but can be 100 times more potent, experts warn, with …
drugdrugabusedrugswithdrug
The Effects Of Drug Abuse On Health
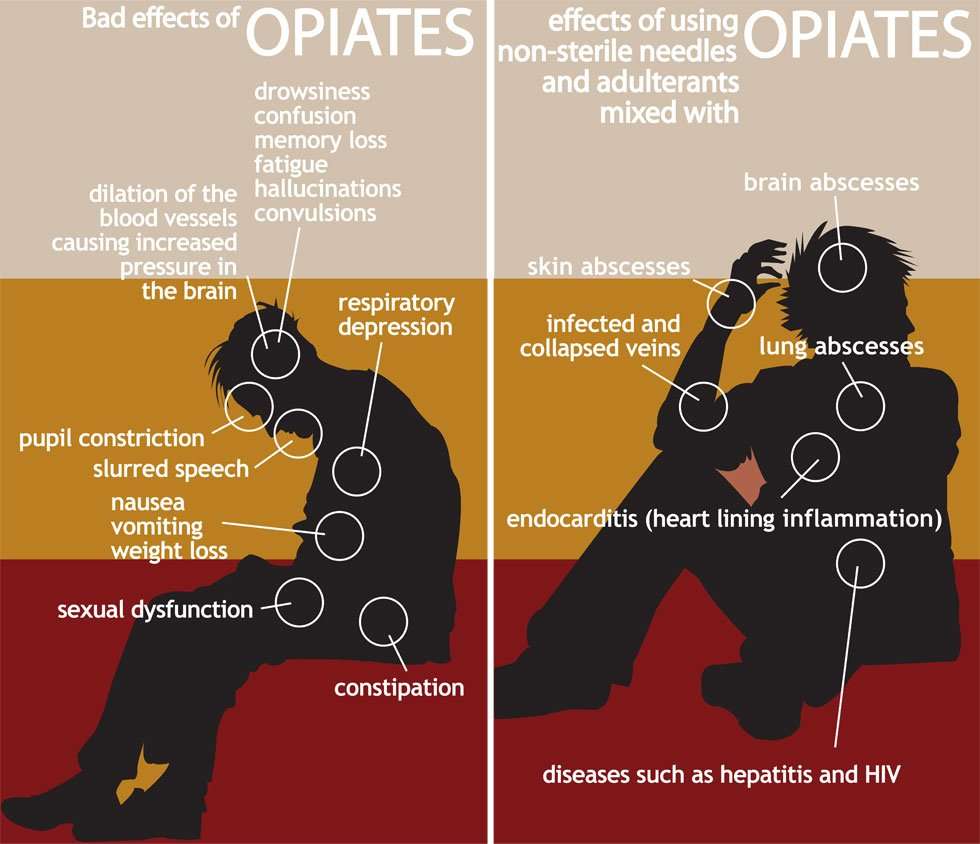
Substance use disorders are associated with a wide range of short- and long-term health effects. They can vary depending on the type of drug, how much and how often its taken and the persons general health. Overall, the effects of drug abuse and dependence can be far-reaching. They can impact almost every organ in the human body.
Side effects of drug addiction may include:
- A weakened immune system, increasing the risk of illness and infection
- Heart conditions ranging from abnormal heart rates to heart attacks and collapsed veins and blood vessel infections from injected drugs
- Nausea and abdominal pain, which can also lead to changes in appetite and weight loss
- Increased strain on the liver, which puts the person at risk of significant liver damage or liver failure
- Seizures, stroke, mental confusion and brain damage
- Problems with memory, attention and decision-making, which make daily living more difficult
- Global effects of drugs on the body, such as breast development in men and increases in body temperature, which can lead to other health problems
The most severe health consequences of drug abuse is death. Deaths related to synthetic opioids and heroin have seen the sharpest rise. In the past 12 months, 212,000 people aged 12 or older have used heroin for the first time. Every day, more than 90 Americans die after overdosing on opioids.
Drug Abuse Vs Substance Use Disorder
This article references the term drug abuse, which is a stigmatizing term. Instead, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition uses the term substance use disorder . The manual defines SUD as a disorder involving the continued use of substances despite personal, professional, and health-related problems caused by the usage that negatively affect a persons day-to-day life.
Generally, drug misuse or SUD refers to the use of psychoactive drugs, which are substances that affect the brain. The effects on the body on the type of substance a person uses and their health history.
Examples of common psychoactive drugs include:
may affect a persons memory, behavior, learning, consciousness, and concentration.
Substances, such as alcohol, cannabis, stimulants, and opioids, are psychoactive drugs that may change an individuals brain function and structure after chronic use. This can resul t in cognitive and behavioral changes and deficits that may remain even after someone stops using.
The exact mental or cognitive effects of SUD may vary depending on the type of drug and the duration of use.
SUD may also exacerbate symptoms of other mental disorders, and early drug use is a strong risk factor for the later development of substance use disorders. It may also be a risk factor for developing other mental illnesses.
Also Check: Can You Get Addicted To Ritalin
Disease Burden From Substance Use Disorders
1.5% of global disease burden results from alcohol and illicit drug addiction in some countries its over 5%
Using the measure of deaths fails to capture the full health consequences of substance use disorders. Drugs not only lead to death, but also to diseases and disabilities that impact peoples health.
To quantify full health impacts we can look at disease burden, measured in Disability-Adjusted Life Years DALYs. This metric considers not only death rates, but also years lived with disability or health burden.
In the map we see the share of disease burden attributed to substance use disorders. 1.5% of global disease burden is attributed to alcohol and illicit drug addiction.
In some countries this share is much higher: in the USA it accounts for more than 5% of disease burden.
What Role Does The Brain Play In Addiction
The brain plays a leading role in addiction, just as it plays a role in all human behavior. The choice to try a drug is a decision that that is centered in the executive portion of the brain, the prefrontal cortex. Once consumed, the drug delivers a powerful stimulus to the nucleus accumbens, a cluster of nerve cells below the cerebral cortex, which responds quickly by releasing a flood of dopamine. The neurotransmitter dopamine is often called the pleasure molecule, but it is more correctly defined as a chemical that underlies motivation. It focuses attention on and drives people to pursue specific goals.
The sensation of pleasure orchestrated by dopamine likely arose to encourage repetition of behaviors that support individual and species survivaleating, interacting with others, having sex. The high level of direct stimulation by drugs of abuse powerfully encourages repetition. Addiction can be seen as hacking the brain by drugsa way to create a direct path to feeling good.
Recommended Reading: How Easy Is It To Get Addicted To Cigarettes
Oral Health Care Interventions For Drug Addicts
Interventions available to drug addicts mainly include oral health education and prevention as first-level care, and delivery of dental services as second-level care. Examples of the former include empowering dentists on the one hand, and health care personnel in drug rehabilitation settings on the other to provide oral health education and prevention for addicts and their families, and to provide educational materials regarding prevention of oral problems. As second-level care: 1) Dental services should be established in addiction rehabilitation centers to improve access to dental treatment. 2) Dentists should be empowered in the following domains to provide treatment services for addicts:
What Do Brain Imaging Studies Show About Addiction
Brain imaging studies reveal which structures of the brain are involved in addiction, the intensity of their involvement, the networks of connectivity between them, how connectivity is configured and reconfigured in response to stimuli, and how the structures and circuitry influence addiction-related behavior.
One of the most notable findings of brain imaging studies of addiction is the degree to which, through dopamine pathways, the prefrontal cortex is consistently dysregulated, disempowered in response to activation of the nucleus accumbens by drug cues. Brain imaging studies help explain how drug cues biologically narrow focus on the substance of abuse, motivate the drive to get it, and impair rational decision-makingbrain changes that make addiction a self-perpetuating condition.
Imaging studies also reveal that many substances of abuse are related to reduction in volume of specific areas of the cerebral cortex, reflecting a pruning of synapses to make the brain highly efficient in drug-seeking. The loss of synaptic density underlies a biologically based inability to respond to the wide range of other, more natural rewards. Ongoing research suggests that imaging studies measuring cortical thickness and brain response to a decision-making task may reveal who is most susceptible to relapse and could benefit from particular types of supportive treatment, such as cognitive therapies that strengthen executive control.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take To Get Over Alcohol Addiction
Challenges In Providing And Implementing Effective Treatments/interventions
Despite evidence as to addicts oral health problems, several barriers exist against provision of preventive and curative interventions. Dental professionals usually have negative attitudes toward and unwillingness to treat addicted dental patients . On the other hand, addicts generally show a low demand for non-emergency dental care and put a low priority on their oral health In addition to the problems with utilization of dental services , they may have problems with compliance with treatment procedures and fail to accept the suggested treatment plan .
Finally, lack of appropriate policies to improve access to oral health services and poor collaboration between dental and general health care sectors serving drug addicts are other obstacles to effective interventions.
Addictive Drugs With Medical Purposes
Drugs can have many medical and mental health benefits when used as directed by a doctor. If you suffer from a medical or mental health condition, medications are often an important part of your treatment and wellness plan. However, prescription drugs can have serious medical complications when abused. Between April 2020 and April 2021, 14,000 Americans died from a prescription opioid overdose. Regular and repeated drug abuse can:
- Damage internal organs
- Lead to the onset of several serious diseases and complications
- Cause poor mental health
- Increase the odds for addiction
The following classes and types of drugs can be medically beneficial, but also have a high potential for abuse:
You May Like: Best Non Addictive Anxiety Medication
Prescription Drug Abuse Problem
For some time now, the abuse of illicit substances such as marijuana, cocaine, methamphetamine and heroin has been a persistent national problem. In more recent years, however, our country has seen an alarming rise of prescription drug abuse – now …
Drug Abusewithdrug abuseassociated problems
Anxiety And Substance Abuse
It can be difficult to manage an anxiety disorder or a substance use disorder, and it can be even more difficult to manage both disorders when they co-occur together. When a mental health disorder, such as an anxiety disorder, and a substance use …
associated withabuseAbuseProblemabuse
Also Check: How To Stop Nicotine Addiction
Whos Most Likely To Become Addicted
Each personâs body and brain are different. People also react differently to drugs. Some love the feeling the first time they try it and want more. Others hate it and never try again.
Not everyone who uses drugs becomes addicted. But it can happen to anyone and at any age. Some things may raise your chances of addiction, including:
- Family history. Your genes are responsible for about half of your odds. If your parents or siblings have problems with alcohol or drugs, youâre more likely as well. Women and men are equally likely to become addicted.
- Early drug use. Childrenâs brains are still growing, and drug use can change that. So taking drugs at an early age may make you more likely to get addicted when you get older.
- Mental disorders. If youâre depressed, have trouble paying attention, or worry constantly, you have a higher chance of addiction. You may turn to drugs as a way to try to feel better. A history of trauma in your life also makes you more likely to have addiction.
- Troubled relationships. If you grew up with family troubles and arenât close to your parents or siblings, it may raise your chances of addiction.
Who Is At Risk For Drug Addiction

Various risk factors can make you more likely to become addicted to drugs, including:
- Your biology. People can react to drugs differently. Some people like the feeling the first time they try a drug and want more. Others hate how it feels and never try it again.
- Mental health problems. People who have untreated mental health problems, such as depression, anxiety, or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder are more likely to become addicted. This can happen because drug use and mental health problems affect the same parts of the brain. Also, people with these problems may use drugs to try to feel better.
- Trouble at home. If your home is an unhappy place or was when you were growing up, you might be more likely to have a drug problem.
- Trouble in school, at work, or with making friends. You might use drugs to get your mind off these problems.
- Hanging around other people who use drugs. They might encourage you to try drugs.
- Starting drug use when you’re young. When kids use drugs, it affects how their bodies and brains finish growing. This increases your chances of becoming addicted when you’re an adult.
Recommended Reading: How To Stop My Addiction To Video Games
Who Is At Risk For Substance Use Disorder
Anyone can develop a substance use disorder. No one thing can predict whether a person may develop an addiction. You may be more prone to drug use due to:
- Biology: The persons genetic makeup, gender, ethnicity and mental health issues may raise his or her risk for developing an addiction. About two-thirds of people in addiction treatment are men. Particular ethnicities are at higher risk for substance use disorder. This is true for Native Americans.
- Environment: Surroundings can affect the likelihood of developing substance use disorder. For example, stress, peer pressure, physical or sexual abuse and early exposure to drugs can raise the risk.
- Age: Teenagers who start taking drugs are especially at risk. The parts of the brain that control judgment, decisions and self-control are not fully developed. Teens are more likely to engage in risky behaviors. In a developing brain, drugs can cause changes that make addiction more likely.
Drug Abuse Vs Drug Addiction
While the terms drug abuse and drug addiction are often used interchangeably, they’re different. Someone who abuses drugs uses a substance too much, too frequently, or in otherwise unhealthy ways. However, they ultimately have control over their substance use.
Meanwhile, someone with a drug addiction abuses drugs in a way that affects every part of their life. They can’t stop misusing drugs even if they want to.
Don’t Miss: Why Is Addiction So Hard To Overcome
Tip : Manage Stress And Emotions
Learn how to manage stress. Drug and alcohol abuse often stems from misguided attempts to manage stress. Stress is an inevitable part of life, so its important to have healthy coping skills so you can deal with stress without turning to alcohol or drugs. Stress management skills go a long way towards preventing relapse and keeping your symptoms at bay.
Cope with unpleasant feelings. Many people turn to alcohol or drugs to cover up painful memories and emotions such as loneliness, depression, or anxiety. You may feel like doing drugs is the only way to handle unpleasant feelings, but HelpGuides free Emotional Intelligence Toolkit can teach you how to cope with difficult emotions without falling back on your addiction.
Know your triggers and have an action plan. When youre coping with a mental disorder as well as a substance abuse problem, its especially important to know signs that your illness is flaring up. Common causes include stressful events, big life changes, or unhealthy sleeping or eating patterns. At these times, having a plan in place is essential to preventing a drink or drug relapse. Who will you talk to? What do you need to do to avoid slipping?
How Does Addiction Hijack The Brain
The very fast and very intense flood of dopamine generated by taking a drug of abuse motivates repetition of the drug-taking. Under the influence of dopamine, that repetition changes the wiring of the brain in ways to increase the drug-wanting and decrease the ability to regulate the drug usage. What starts as a choice becomes so deeply wired into the brain that the machinery of desire operates automatically, and the machinery of attention narrows focus to the drug and getting it. The brain loses the capacity to respond to other potentially rewarding activities. The desire for reward ultimately becomes a prison from which it is difficultbut not impossibleto escape.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take To Break Alcohol Addiction
Warning Signs Of Drug Abuse
Use of recreational drugs, over the counter medications or prescription drugs can lead to substance use issues. It can frequently lead to problems at work, home, school, and in relationships, and leave the user feeling isolated, helpless, or shamed. If youre worried about your own or a loved ones drug use, its helpful to know the warning signs and more importantly, that help is available and treatment works.
Common signs and symptoms of drug abuse
- Risk taking when youre using, such as driving, having unprotected sex
- Neglecting responsibilities at school, work, or home
- Legal trouble, such as arrests for disorderly conduct, driving under the influence
Physical warning signs of drug abuse
- Bloodshot eyes, pupils larger or smaller than usual
- Changes in appetite, sleep patterns, physical appearance
- Unusual smells on breath, body, or clothing, or impaired coordination
Behavioral signs of drug abuse
- Drop in attendance and performance at work or school
- Engaging in secretive or suspicious behaviors
- Sudden change in friends, favorite hangouts, and hobbies
Psychological warning signs of drug abuse
- Unexplained change in personality or attitude
- Sudden mood swings, irritability, spaced-out, or angry outbursts
- Appears fearful, anxious, or paranoid, with no reason
For immediate help and information on treatment, contact the RedlinePhone: 889-9789
Psychological Issues Resulting From Addiction
It is commonplace that the abuse of alcohol and drugs result in an unbalanced mental state in many people. For some, it amplifies a preexisting mental health condition like depression and anxiety. For some others, alcohol and drug addiction set off the psychological issue. This effect is mainly ascribed to psychoactive substances like alcohol, cocaine, and heroin which significantly impact the brain and nervous system. These substances induce feelings like loneliness, depression, and confusion/delirium in the user once the high has worn off. Sometimes, suicidal thoughts may set in.
Don’t Miss: Am I Addicted To Masterbating
Health Conditions And Illnesses Caused By Drug Addiction
January 25, 2022 by Melissa Bell
In 2017, there were 70,237 drug overdose deaths in the United States.
Repeated drug abuse has both short-term and long-term health consequences. Specific consequences of drug addiction vary depending on the person, the amount used, the persons medical history, and, of course, the substance used.
Addiction victims frequently have one or more co-occurring health issues, including lung or heart disease, stroke, cancer, or mental health issues.
Furthermore, some drugs, such as inhalants, can harm or destroy nerve cells in the brain. Infinite Recovery drug rehab center takes care of these health issues. If you want to know more about them, click .
What Are Symptoms Of Substance Use Disorder

Symptoms of drug addiction include:
- Bloodshot eyes and looking tired.
- Changes in appetite, usually eating less.
- Changes in physical appearance, such as having a poor complexion or looking ungroomed.
- Difficulty completing tasks at work, school or home.
- Engaging in risky behaviors, despite knowing negative consequences .
- Inability to reduce or control drug use.
- Issues with money.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop An Addiction To Food
