The Science Of Nicotine Addiction
PRINT THIS PAGE
The news made headlines in 2006: Smokers today get more nicotine from inhaling cigarette smoke than they did in 1998. The news is alarming because nicotine is the chemical in cigarette smoke that causes addiction to tobacco. The Massachusetts Department of Public Health reported its discovery that the nicotine yield in cigarettesmeaning the amount of nicotine a smoker gets from a cigarettehad increased steadily between 1998 and 2004. The DPH used information provided by tobacco companies themselves.
One deadly consequence of more nicotine yield in cigarettes is that the average smoker will find it harder to quit. Not only is there more nicotine in cigarettes, but nicotine itself is a powerfully addictive drug. In the words of a NIDA-funded researcher, Dr. Daniel McGehee: “It would be difficult to design a better drug to promote addiction.”
Why Nicotine Is So Addictive In investigating the addictive power of nicotine, NIDA-funded researchers at the University of Chicago found that nicotine’s effect on the brain is doubly dangerous. It directly stimulates the feelings of pleasure and indirectly keeps those pleasurable feelings going strong.
To explain why dopamine levels remain high after direct nicotine stimulus ends, researchers looked at two other neurotransmitters in the brain, glutamate and GABA. Glutamate is a neurotransmitter that speeds up the activity of neurons. GABA is a neurotransmitter that slows down neuron activity.
Vaping Vs Regular Cigarettes
Weighing the pros and cons of vaping versus smoking is difficult to do. On the one hand, e-cigarettes likely do not produce 7,000 chemicalssome of which cause cancerwhen they are activated, like regular combustible cigarettes do. However, the aerosol from a vape device has not been proven safe. Studies have found that it contains lead and volatile organic compounds, some of which are linked to cancer. Researchers are still gathering data on the possible long-term health effects from vaping. Its notable that e-cigarettes have not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration as smoking cessation devices. However, e-cigarettes may be a better choice for adult smokers if they completely replace smoking, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
But where nicotine levels are concerned, a newer and popular type of vape device, called a pod mod, outcompetes many other e-cigarette devices. The form of nicotine in these pods is estimated to be 2 to 10 times more concentrated than most free-base nicotine found in other vape liquids. A single pod from one vape manufacturer contains 0.7 mL of nicotine, which is about the same as 20 regular cigarettes.
Despite its extremely addictive nature, people can successfully quit using nicotine with personalized approaches, especially under the guidance of physicians who understand addiction.
Psychoactive Effects Of Nicotine
Nicotine induces pleasure and reduces stress and anxiety. Smokers use it to modulate levels of arousal and to control mood. Smoking improves concentration, reaction time, and performance of certain tasks. Relief from withdrawal symptoms is probably the primary reason for this enhanced performance and heightened mood. Cessation of smoking causes the emergence of withdrawal symptoms: irritability, depressed mood, restlessness, and anxiety. The intensity of these mood disturbances is similar to that found in psychiatric outpatients. Anhedonia the feeling that there is little pleasure in life can also occur with withdrawal from nicotine, and from other drugs of abuse.
The basis of nicotine addiction is a combination of positive reinforcements, including enhancement of mood and avoidance of withdrawal symptoms . In addition, conditioning has an important role in the development of tobacco addiction.
Molecular and Behavioral Aspects of Nicotine Addiction
Also Check: Is Drug Addiction Grounds For Divorce
Stress And When To Avoid Nicotine
Many people smoke tobacco as a way to relieve stress. While this is not a great choice for health, it does point to an underlying need to address the stress that is reinforcing the craving for tobacco.
Constant stress can lead to exhaustion. Feeling fatigued almost everyday, along with symptoms of insomnia, brain fog, anxiety, reduced concentration, brain fog, difficulty in waking up, low energy levels, fatty and salty food cravings, difficulty dealing with stress, irritability, and constipation can point to Adrenal Fatigue Syndrome .
During stress, the HPA axis and NeuroEndoMetabolic Stress Response activate hormonal systems to protect your body from excess stress. Several major systems of the body make up the NEM system. These include the adrenal glands, which secrete several hormones under stress including cortisol to help deal with the stress. But when the stress is constant, the adrenals need to secrete more cortisol to handle it. Over a long enough period, the adrenals get overburdened and lose their ability to secrete adequate cortisol. Consequently, your body finds it difficult to address stressful situations.
Though smoking is sometimes used to deal with stress, and in spite of the various benefits of nicotine, both smoking and nicotine alone are not recommended for those with adrenal fatigue. If you have been under chronic stress and may have adrenal fatigue issues, it is advisable to avoid nicotine.
There are several ways nicotine can worsen AFS symptoms.
Cigarettes’ Power May Not Be In Nicotine Itself New Study Suggests

- Date:
- Kansas State University
- Summary:
- New research suggests that cigarettes’ power may not be in nicotine itself but in how it enhances other experiences while smoking.
There may be a very good reason why coffee and cigarettes often seem to go hand in hand.
A Kansas State University psychology professor’s research suggests that nicotine’s power may be in how it enhances other experiences. For a smoker who enjoys drinking coffee, the nicotine may make a cup of joe even better.
And that may explain why smoking is so hard to quit.
“People have very regimented things they do when they smoke,” said Matthew Palmatier, assistant professor of psychology at K-State. “If you think about where people smoke or who they smoke with, you realize that it occurs in very specific places, often with a specific group of people. Maybe it’s a reason why nicotine is so addictive if you get used to having that extra satisfaction from things you normally enjoy, not having nicotine could reduce the enjoyment in a given activity.
“People may not be smoking to obtain a pleasurable drug state. They may be smoking in order to regulate their mood, and that effect could make nicotine more addictive than other drugs.”
Palmatier said much previous research on nicotine addiction has looked at the drug itself rather than the other factors he is studying.
“The approach we’re taking is out of left field,” he said. “But it seems to be one of the best explanations as to why people smoke.”
Story Source:
Don’t Miss: How To Get Off Pain Medication Addiction
Nicotine Side Effects On All Systems In The Body
Nicotine has adverse effects on every bodily system. Some of these develop over time but some are present with every dose of nicotine you take.
Nicotine Effects: Central Nervous System
- Dyspepsia
- Cancer
Mentioned health effects can all be attributed to nicotine but are greatly exacerbated by other compounds usually found in tobacco products, such as tar, carbon monoxide, toluene, or any of the other 4,000 substances regularly found in cigarettes.
How Long Does Nicotine Stay In Your System
Nicotine is mostly absorbed into the body through the lungs as well as the membranes in the mouth and throat. It can also be absorbed in your gastrointestinal tract or your skin if you use a nicotine patch.
Nicotine is mainly metabolized in the liver and is excreted via urine through the kidneys as well as in feces. How long it stays in your system depends on many factors, including age, weight, type, frequency of use, and hydration and physical activity levels.
That said, the estimated timeframe is as follows:
- Urine test: Two to four days
- Blood test: Two to four days
- Saliva test: One to four days
- Hair follicle test: Up to 90 days
Many routine drug tests screen for nicotine.
You May Like: Why Do People Have Addictive Personalities
Even When Cassie Was In Hospital With A Collapsed Lung She Got Her Friend To Push Her Outside For A Cigarette
The funniest thing is when you can smoke anywhere I think in a way its less ritualistic. You know, youve got your first one, your last one of the day, but if, if you can light up and smoke wherever you are, theres, theres kind of less pressure on you to smoke now. Whereas if you have to go out of the building to smoke, you begin to think, oh I havent had a cigarette for 40 minutes. Oh I wonder if, now if I stopped doing what Im doing now, I can take a 5 minute break or a ten minute break. If I can a ten minute break I can smoke two.
So youre, youre planning all the time, youre sort of, planning your day around your cigarette breaks and I think in a way its less productive, because its on your mind all the time. Is like if youre on a diet and you think about food all the time, whereas if youre not on a diet you dont think about food at all. And it, its hard to give you a, a sort of what my smoking day was like from the days when you smoke anywhere, because it just wherever you fancied a cigarette. It was far more planned in the years since it became more difficult to smoke.
Nicotine And Neurotransmitter Release
Stimulation of nicotinic cholinergic receptors releases a variety of neurotransmitters in the brain., One of them, dopamine, signals a pleasurable experience and is critical for the reinforcing effects of nicotine and other drugs of abuse, as well as for compelling drives such as eating. Experimentally induced lesions in dopamine-releasing neurons prevent self-administration of nicotine in rats. Nicotine releases dopamine in the mesolimbic area, the corpus striatum, and the frontal cortex . The dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area of the midbrain and in the shell of the nucleus accumbens are critical in drug-induced reward .,
Role of the Mesolimbic Dopamine System in Nicotine Activity
Nicotine activates 42* receptors in the ventral tegmental area, resulting in dopamine release in the shell of the nucleus accumbens.
Nicotine also augments both glutamate release, which facilitates the release of dopamine, and -aminobutyric acid release, which inhibits dopamine release., With long-term exposure to nicotine, some nicotinic cholinergic receptors become desensitized but some do not. As a result, GABA-mediated inhibitory tone diminishes while glutamate-mediated excitation persists, thereby increasing excitation of dopaminergic neurons and enhancing responsiveness to nicotine.
You May Like: How To Stop My Sugar Addiction
Research Suggests Vaping Is Bad For Your Heart And Lungs
Nicotine is the primary agent in both regular cigarettes and e-cigarettes, and it is highly addictive. It causes you to crave a smoke and suffer withdrawal symptoms if you ignore the craving. Nicotine is also a toxic substance. It raises your blood pressure and spikes your adrenaline, which increases your heart rate and the likelihood of having a heart attack.
Is vaping bad for you? There are many unknowns about vaping, including what chemicals make up the vapor and how they affect physical health over the long term. People need to understand that e-cigarettes are potentially dangerous to your health, says Blaha. Emerging data suggests links to chronic lung disease and asthma, and associations between dual use of e-cigarettes and smoking with cardiovascular disease. Youre exposing yourself to all kinds of chemicals that we dont yet understand and that are probably not safe.
Why Cant My Teen Quit Smoking Or Vaping
Because their brains are still developing, young people have a higher risk of becoming addicted to the nicotine in tobacco products than adults.
Many teens dont understand how easy it is to become addicted to tobacco products. The younger a person is when they start using tobacco, the more likely they are to become addicted.7
Nicotine exposure during adolescence can disrupt normal brain development and may have long-lasting effects, such as increased impulsivity and mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorder.7
Because of nicotines powerfully addictive nature and major effects on the developing brain, no tobacco products are safe for youth to use.
If youre trying to teach your children or students about the dangers of tobacco use, there are tobacco education resources for parents and teachers that can help.
Read Also: How Are Video Games Addictive
Nicotine Side Effects On Your Brain
Cigarettes are one of the fastest ways to get nicotine into your system. After an inhale, tar with nicotine deposits travels to lungs where it latches on and gets absorbed by the organism. It takes up to twenty seconds for nicotine to travel to the brain. Other delivery methods, such as chewing tobacco, smokeless tobacco, and e-cigarette systems are slower, but not by much.
When nicotine reaches the brain it attaches to neural receptors usually reserved for acetylcholine. This begins a series of chain reactions in the body. First, it starts to stimulate the adrenal glands which start releasing large amounts of adrenaline into the system. This flight or fight hormone elevates the heart rate and breathing. As the heart rate goes up so does the blood pressure and this means that nicotine is also partly to blame for numerous vascular diseases.
That rush of adrenaline also signals the body to dump sugars into the system under normal circumstances that sugar would be useful for either the fight or the flight response. In this case, it stays in the bloodstream, accumulating and since nicotine suppresses insulin release this means that smokers regularly have elevated blood sugar levels. High blood sugar is one of the reasons why smokers tend not to feel hungry after a cigarette, regardless of how long it was since their last meal.
Recent Research Sheds New Light On Why Nicotine Is So Addictive
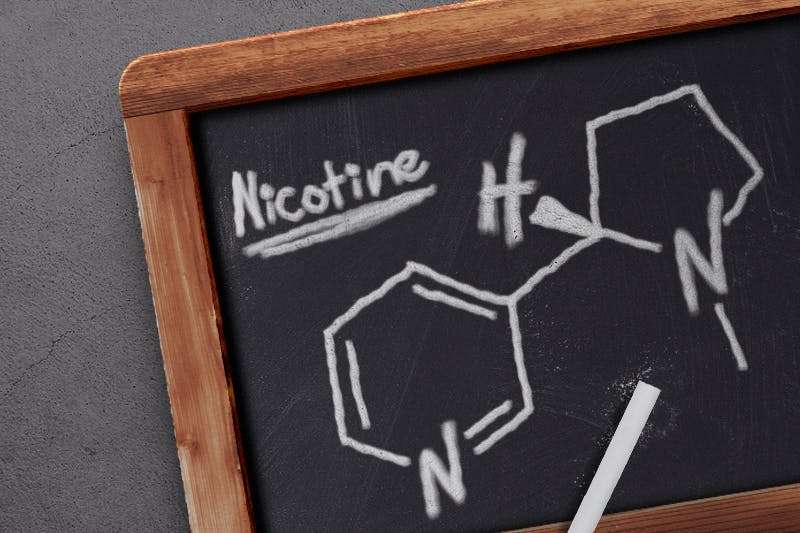
Although our society currently finds itself focused on the tragic epidemic of opioid overdoses, there remains no better example of the deadly power of addiction than nicotine. The measure of a drugs addictiveness is not how much pleasure it causes but how reinforcing it isthat is, how much it leads people to keep using it. Nicotine does not produce the kind of euphoria or impairment that many other drugs like opioids and marijuana do. People do not get high from smoking cigarettes or vaping. Yet nicotines powerful ability to reinforce its relatively mild rewards results in 480,000 deaths annually.
But research continues to provide new insights into the reinforcing effects of nicotine, and we now know that nicotines insidiousness as a reinforcer goes beyond its ability to promote smoking , extending to other non-nicotine drugs and even to non-drug rewards.
This secondary reinforcing effect may contribute to the difficulty smokers have when trying to quit. It is not simply that they crave nicotine and feel withdrawal symptoms in its absence. It is also that other activities are not as enjoyable or motivating to them in the absence of nicotine. This is valuable knowledge that may help us design new prevention strategies and smoking cessation treatments.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Medical Model Of Addiction
Why Do People Start Smoking
Most people who smoke started smoking when they were teenagers. Those who have friends and/or parents who smoke are more likely to start smoking than those who dont. Some teenagers say that they just wanted to try it, or they thought it was cool to smoke.
The tobacco industrys ads, price breaks, and other promotions for its products are a big influence in our society. The tobacco industry spends billions of dollars each year to create and market ads that show smoking as exciting, glamorous, and safe. Tobacco use is also shown in video games, online, and on TV. And movies showing people smoking are another big influence. Studies show that young people who see smoking in movies are more likely to start smoking.
A newer influence on tobacco use is the e-cigarette and other high-tech, fashionable electronic vaping devices. Often wrongly seen as harmless, and easier to get and use than traditional tobacco products, these devices are a way for new users to learn how to inhale and become addicted to nicotine, which can prepare them for smoking.
So Why Is Nicotine So Addictive For Teens
Nicotine can spell trouble at any life stage, but it is particularly dangerous before the brain is fully developed, which happens around age 25.
Adolescents dont think they will get addicted to nicotine, but when they do want to stop, they find its very difficult, says Yale neuroscientist Marina Picciotto, PhD, who has studied the basic science behind nicotine addiction for decades. A key reason for this is that the adolescent brain is more sensitive to rewards, she explains.
The reward system, called the mesolimbic dopamine system, is one of the more primitive parts of the brain. It developed as a positive reinforcement for behavior we need to survive, like eating. Because the mechanism is so engrained in the brain, it is especially hard to resist.
When a teen inhales vapor laced with nicotine, the drug is quickly absorbed through the blood vessels lining the lungs. It reaches the brain in about 10 seconds. There, nicotine particles fit lock-and-key into a type of acetylcholine receptor located on neurons throughout the brain.
You May Like: How To Fight Marijuana Addiction
Are There Other Chemicals That May Contribute To Tobacco Addiction
Research is showing that nicotine may not be the only ingredient in tobacco that affects its addictive potential.
Smoking is linked with a marked decrease in the levels of monoamine oxidase , an important enzyme that is responsible for the breakdown of dopamine, as well as a reduction in MAO binding sites in the brain.42 This change is likely caused by some as-yet-unidentified ingredient in tobacco smoke other than nicotine, because we know that nicotine itself does not dramatically alter MAO levels.Animal research suggests that MAO inhibition makes nicotine more reinforcing, but more studies are needed to determine whether MAO inhibition affects human tobacco dependence.42
Animal research has also shown that acetaldehyde, another chemical in tobacco smoke created by the burning of sugars added as sweeteners, dramatically increases the reinforcing properties of nicotine and may also contribute to tobacco addiction.43
