Addiction Changes The Brains Chemistry
Good communication is absolutely important, functioning as the major key to coordinate with family members or people from work. Our bodies are no different. Neuron systems deliver messages back and forth within the structures of the spinal cord, nerves and the brain. These complex networks regulate and interpret everything that we feel, see, think and do.
To understand the effect of addiction on the brain system, one must understand how communication works. Communication systems consist of five senses, namely:
- sight
- smell
These five senses collect and analyze information around us the brain processes all these.
As a complex organ, the brain receives a massive amount of information. It may sound complex but the brain works on a simple electrochemical process.
The communication system works allowing the brain to interact with the other body parts. Billions of neurons passed the information to the brain. Human brains contain billions of these neurons connections. The massive network builds an electrochemical communication system.
Some neurotransmitters can affect other neurons . They can affect other neurons and produce reactions. Here are some of the neurons found in the brain.
- Inhibitory neurons prevents the next neuron from sending another reaction.
- Glutamate the most common excitatory neurotransmitter found in the brain.
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid or GABA the most common inhibitory. This plays an important role in addiction.
Drugs and its affected brain system
Brain Therapies For Addiction
When someone battling addiction enters a facility, they receive medication and have access to innovative treatments. A common treatment to stabilize and soothe the brain after addiction is biofeedback therapy. This allows a professional to monitor the brain. They can figure out how to improve brain activity, reducing the effects of addiction and unhealthy impulses.
Biofeedback uses electroencephalograms . EEGs are typically used to help individuals who have suffered traumatic brain injuries and can be helpful to individuals with obsessive compulsive disorder and other brain disorders. Biofeedback reduces stress and reduces involuntary functions. This therapy can also include meditation, guided imagery, and muscle relaxation.
When this is combined with therapies like cognitive behavioral therapy or dialectical behavioral therapy , biofeedback improves the individuals involuntary functions, like heartbeat, blood pressure, and muscle contraction. Neurofeedback, or EEQ therapy, is a type of biofeedback. This therapy is a brain-training treatment. In the case of addiction, this therapy monitors the brains activity. It helps patients to reduce stress and anxiety and can treat compulsions. The end result of both therapies is the administrator rewarding the brain to recover how it functions.
How Long Does It Take For The Brain To Recover From Addiction
Most people are surprised at how quickly they feel better once they get past initial withdrawal symptoms. Within a few days, most people feel less cloudy and have more positive energy. The timeline depends on
Dont get discouraged. It may take months before you feel completely back to normal, but youll feel better as you make progress along the way.
You can break down brain recovery into three parts:
- Dopamine Production: Drugs trigger a dopamine release Abused substances trigger dopamine production at high levels and a rapid pace. Over time, the brain learns to stop producing dopamine naturally and must relearn to do so.
- Retraining the Brain: This may mean eliminating habits that pull the individual towards addiction, engaging in new thought patterns, or teaching it to respond differently to stimuli.
- Cravings: The desire to use is most intense during your first few days sober. Over time, cravings are reduced to passive thoughts that are easily shaken off.
No one becomes addicted to drugs and alcohol overnight, and just the same it takes time for the brain to heal from addiction. Be patient and trust the process.
Read Also: What Does Rehab Do For Drug Addicts
The Powerful Influencing Effects Of Addiction
Addiction influences the brain on various levels. Every substance has different compounds, and the way they affect the brain depends on the chemical compounds in these substances like sedatives, alcohol, opioids, or nicotine.
The moment these compounds enter the system, they will penetrate the bloodstream and get transported all the way to the brain. Addiction has a long and strong influence on the brain that is recognizable in three different ways:
- Insatiable cravings for substances
How Does Addiction Affect The Body And Brain
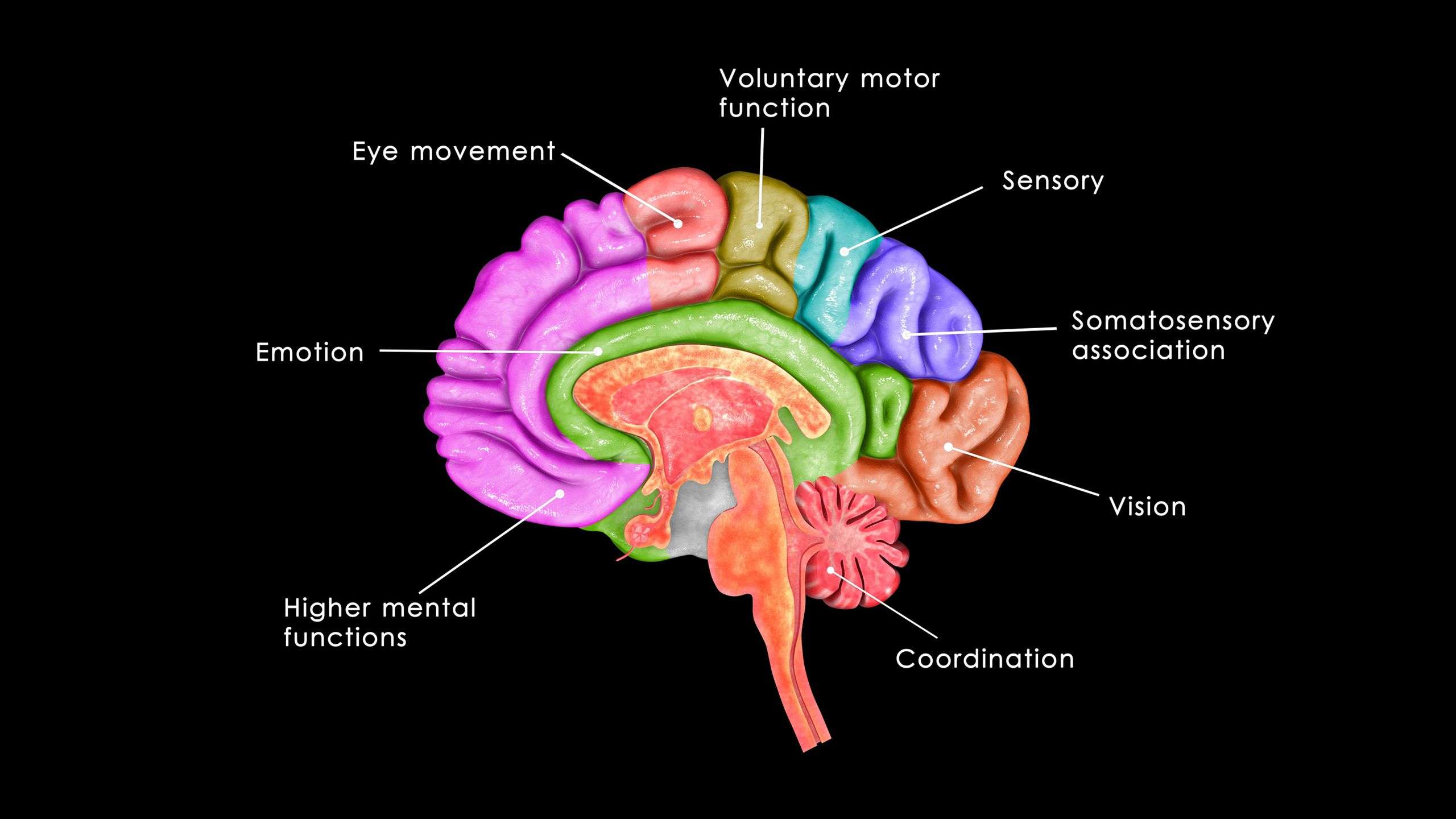
Home> How does addiction affect the body and brain?
An addiction is a serious brain condition, impacting one of the most vital organs in the body. It also affects the body itself, from how it functions to its wellbeing.
Whilst signs and symptoms of addiction are regularly displayed on the outside, the majority of effects and damages are happening on the inside.
Throughout the development phases of addiction, health and wellbeing can begin to slip. Drugs and alcohol interfere with how the body and brain operate, communicate, and survive. Over time, interferences can cause many health conditions, can result in irreversible damages and can flaw the biochemistry of the brain.
Very difficult to overcome, an addiction is an ingrained condition, which can relapse if untreated or mistreated. As both the body and brain are highly adaptive, they will continue to accommodate drugs and alcohol. Lapsing habits, behaviours and consumption levels will be essential, to bounce back physically and mentally.
Heres the truth behind how does addiction affect the body and brain?, along with the treatability of addiction. At Rehab Clinics Group we can help to treat and get your addiction under control, ready to elevate your physical and mental health.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Chewing Tobacco Addiction
How Does Addiction Happen
Addiction begins with desire. Some people use addictive substances to escape emotional, psychological, or physical pain, while others use drugs and alcohol to relax or cope with family, school, financial, and career pressure. Other reasons for substance use include boredom, a need for instant gratification, a desire for rebellion, peer pressure, curiosity, or a need to feel in control. All of these reasons are rooted in desire. Drugs and alcohol seem to satisfy users desire by evoking the brains pleasure center.
Long Term Addiction Treatment
Alongside holistic therapies and wellbeing management, traditional treatment must be completed to recover from addiction for the long term. The aim through this combination is to withdraw from drugs and alcohol, support the body and brain through the process, learn to cope without their presence, and improve wellbeing to unwelcome future abuse.
Detoxification and rehabilitation will be recommended, to get clean, develop new outlooks, routines, and habits, and improve mental health. Each treatment session will focus on rebuilding post-addiction, to sustain sober intentions, feelings, and choices.
Relapse prevention planning will be key to protecting the body and brain. Plans will be in place to avoid psychological triggers, suppress physical actions of consumption, and improve overall wellbeing.
Its clear that by answering how does addiction affect the body and brain?, that it is a significant disorder that can disrupt, damage, and gain physical and psychological control. If youre struggling, at Rehab Clinics Group, we can help you experience suitable support and treatment to regain control. Heal your body and brain whilst protecting them for the future through addiction treatment.
Alcohol Addiction
Don’t Miss: How To Deal With Alcohol Addiction
Adolescence Brain Change And Vulnerability To Substance Use Disorders
Although young people are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of substance use, not all adolescents who experiment with alcohol or drugs go on to develop a substance use disorder. Prospective, longitudinal studies are needed to investigate whether pre-existing neurobiological factors contribute to adolescent substance use and the development of substance use disorders, how adolescent substance use affects brain structure and function, and whether the changes in brain structure and function that accompany chronic substance use can recover over time. Studies that follow groups of adolescents over time to learn about the developing human brain should be conducted. These studies should investigate how pre-existing neurobiological factors contribute to substance use, misuse, and addiction, and how adolescent substance use affects brain function and behavior.
Why Is The Brain Disease Model Of Addiction So Controversial
There are numerous reasons why people find the brain-disease model of addiction controversial. In the past, people thought that addiction was a moral failing, something that bad people engage in rather than a disease like any other. This is untrue for multiple reasons.
- It ignores or minimizes the role that society plays in addiction
- It doesnt account for environmental factors
- It looks at how addicted brains are different after substance abuse, not before
- It neglects the importance of learning and memory in the addiction process
Over the years, the medical view of addiction has challenged these ideas and proved that being addicted is not about willpower.
Despite the facts, some people still treat addiction as if it were a choice. Today, addiction specialists use the biopsychosocial framework, which accounts for the complex relationships between biology, behavior, and environment.
You May Like: Can You Be Addicted To Xanax
Chemistry In The Human Brain
The human brain is a huge mass of nerve cells that communicate with each other through electrical signals. In addition, there are chemical messengers in the brain called neurotransmitters. Each neuron stores these chemicals in small vesicles near its tail section. It releases these chemical sacs when it sends a signal to the next cell. These chemicals then bind to sites on the next neuron, causing it to either send a signal or not.
These neurotransmitters have a specific effect when they bind to proteins called receptors in nerve cells, similar to how a key fits a lock.
A neurotransmitter can either excite a nerve cell, causing it to send a signal, or it suppresses or prevents the transmission of a signal by a nerve cell.
A good example of an excitatory substance is glutamate, and GABA is an inhibitory neurochemical.
Some parts of the brain are specific in choosing neurotransmitters. For example, cells in an area called the substantia nigra use dopamine to transmit signals. Therefore, they are called dopaminergic neurons. In other parts of the brain there is a mixture of cells in which different types of neurotransmitters are involved.
Addiction And Your Life
Once an addiction to alcohol or drugs takes hold, it becomes the priority in a persons life. If you were addicted to substances, you would find yourself spending more time and money acquiring and using your drug of choice. This means you would have less time for activities you used to enjoy, such as sports and hobbies.
You may even decide to stay away from family events and beg off from plans you had previously made with your family to get drunk or high. It also gets more difficult to keep up your regular schedule and keep your addiction fed you will need time to recover from being drunk or high.
The addiction will also likely take a toll on your work or school life. Your attendance and work performance may suffer since your full attention will not be on your employment duties or studies.
Alcohol and drug use to the point of intoxication puts you at increased risk of injury, both at home and on the job. You are also at increased risk of being involved in a car accident, which could lead to serious injuries to yourself or others.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take To Stop An Addiction
Impaired Control And Judgment Problems
ASAM says that behavioral manifestations and complications of addiction, due to impaired control, can include:
- Engaging in more addictive behavior than you intended
- Increased time lost from work or school
- Continued substance use despite physical or psychological consequences
- Narrowing of your addictive behavior repertoire for instance, you only drink one brand of a certain type of alcohol
- Lack of readiness to get help, despite admitting a problem
How Does An Addiction Develop

When looking into how does addiction affect the brain, its imperative to know that the brain is intimately involved in the process of addiction, much so than the body itself. When someone takes drugs, including prescription medications like opioid painkillers and benzodiazepines used to treat depression, these substances impact the brain. Over time, those brain changes can lead to addiction, primarily if the drugs are used to excess or taken outside the oversight of a physician.
Addiction can develop slowly over time, or it can manifest more quickly than anyone would think. Even if you only think you are developing an addiction or dependency, it is essential to reach out for help as soon as possible.
Also Check: Is Flonase Addictive Like Afrin
Retraining The Brain After Addiction
Even if people understand the changes and cycle of addiction and how it changes the brain, they cannot stop on their own. The brain is dependent on drugs or alcohol, so a person needs to commit to recovery to change his or her lifestyle. When in treatment, a persons brain needs to be re-trained to function normally, without toxic substances. It will take time for the brain to re-adjust to a sober, healthy lifestyle.
At Corner Canyon Health Centers, we focus on the Gut-Brain connection to restore adequate levels of serotonin and dopamine in the brain. Its our top priority to heal the brain after someone has suffered from addiction.
Rewarding The Brain: How Addictions Develop
The brain regulates temperature, emotion, decision-making, breathing, and coordination. This major organ of the body also impacts physical sensations in the body, cravings, compulsions, and habits. Under the influence of a powerful and harmful chemical, individuals abusing substances like Benzodiazepines or Heroin can alter the function of their brain.
Drugs interact with the limbic system in the brain to release strong feel-good emotions, affecting the individuals body and mind. Individuals continue taking drugs to support the intense feel-good emotions the brain releases this creates a cycle of drug use and intense highs. Eventually, they take the drug just to feel normal.
Read Also: Can You Be Addicted To Depression
What Parts Of The Brain Are Affected By Drug Use
Drugs can alter important brain areas that are necessary for life-sustaining functions and can drive the compulsive drug use that marks addiction. Brain areas affected by drug use include:
Some drugs like opioids also disrupt other parts of the brain, such as the brain stem, which controls basic functions critical to life, including heart rate, breathing, and sleeping. This interference explains why overdoses can cause depressed breathing and death.
Heroin And Prescription Opioids
Heroin and prescription opioid drugs like OxyContin , Vicodin , fentanyl, methadone, and Dilaudid bind to opioid receptors in the brain and trigger the release of dopamine. In a sense, these drugs hijack the limbic system in the brain, inducing a powerful high that individuals are often keen to recreate, leading to reinforcing behaviors. Opioid drugs are considered highly addictive, as ASAM publishes that almost a quarter of heroin users will suffer from addiction to opioids. Over 2.5 million Americans battled opioid addiction in 2015. Heroin is considered the fastest-acting opioid, taking effect nearly immediately and making it extremely addictive, the Drug Enforcement Administration warns. When someone takes an opioid drug repeatedly, they can develop a tolerance to it as the body gets used to its interaction in the brain. Individuals may then take more of the drug to feel the desired effects. The brain will then stop functioning as it did before introduction of the opioid, causing levels of dopamine to drop when the drug wears off.
Dependence on opioids can form rather quickly. Physical withdrawal symptoms may resemble the flu, and emotional withdrawal symptoms include depression, anxiety, and insomnia.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Signs Of Opiate Addiction
Addiction Treatment At Resurgence
It does not matter how old you are, how much money you earn, or where you live you only get one brain, and taking care of the gray matter between your ears is essential for your mental, physical and emotional health. Using drugs can impact the brain in many different ways, damaging certain neurotransmitters and even changing the way the mind works.
If you or someone you care about has been struggling with addiction, are wondering how does addiction affect the brain, it is essential to get them help as quickly as possible. Unlike other parts of the body, brain tissue can be slow to regenerate, and many times those damaged neurons will never be restored to total health. That means the sooner you get help, the better off the brain will be, and we do not want you to let anything stand in your way. So pick up the phone today, give the staff at Resurgence a call at and take the first step on the road to a healthier brain and a better life.
How Addiction Affects The Brain
The specifics of addiction vary from one drug to the other, but the most addictive drugs have various similarities. Broadly speaking, they act as neurotransmitters, a type of compound that sends messages in the brain. Antidepressants, opioids, antipsychotics, and other mood-affecting drugs send signals within the brain that serve to modulate your internal state. Some affect the way that serotonin and dopamine interact with your neuroreceptors to help you feel happy. Similar neural relationships between drugs and your brain can dull pain, create a sense of euphoria, and much more.
However, the danger of addiction comes from the fact that these drugs interact with your reward system and have the potential to hijack it. With time, your brain adjusts itself to functioning alongside the drugs. While even responsible use of prescription drugs entails some level of drug tolerance, addicts experience an unhealthy level of tolerance. Once they reach this point, it wont be possible to even feel normal without the drugs. Rather, an addicts brain chemistry will cause them to exist in a perpetual state of misery and unease when theyre separated from the drug.
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Being Addicted To Video Games
Drugs As Neurotransmitter Mimics
Many drugs mimic natural neurotransmitters in the brain. These natural chemicals lead to pleasurable feelings, such as relaxation and euphoria, so drugs that mimic specific neurotransmitters cause similar effects. Heroin, prescription opioids and marijuana all work in ways similar to neurotransmitters.
