When To Call A Doctor
Opiate withdrawal can be a frustrating process with symptoms that, while typically not life threatening, are difficult to manage. Your doctor can help you to manage the symptoms you may experience with personalized recommendations and prescription medications to ease the process. They can also run tests like blood work to evaluate any damage to your system caused by the opiates.
Medications that can be used to treat opiate withdrawal include:
- methadone, which helps to relieve withdrawal symptoms and makes the detoxification period easier
- buprenorphine, which can shorten the time of the detox period and lessen withdrawal symptoms
- clonidine, which can treat symptoms like anxiety, agitation, and muscle aches
If you are worried about your symptoms, or know that you wont be able to make it through withdrawal alone, consult your doctor or find a rehab facility for help.
If you experience nausea or vomiting, you may become dehydrated. Its important to seek medical treatment. Dehydration can be a serious problem leading to abnormal heartbeats, which in rare cases can lead to circulatory and heart problems.
Symptoms of dehydration include:
Why Is The Opioid Crisis So Pervasive In The Us
As we understand it today, the Opioid epidemic has occurred in 3 waves in the US. According to the Centers For Disease Control And Prevention , the first wave occurred in the 1990s when doctors began overprescribing prescription Opioids because pharmaceutical companies told them that the pills were less addictive than Painkiller alternatives. We now know that Opioids are incredibly addictive, and overdose deaths involving prescription Opioids have increased since 1999.
The second wave of rapid overdose deaths involved Heroin in 2010. The third wave, which is where the US is currently, began in 2013. The CDC has reported a significant increase in overdose deaths involving Synthetic Opioids . In fact, the Synthetic Opioid-related overdose death rate was 18 times higher in 2020 than in 2013. Fentanyl is 50 times more potent than Heroin, but drug dealers still combine the substance with Heroin, counterfeit pills, and Cocaine to increase potency, cut costs, and boost profits. If an individual unknowingly takes a substance cut with Fentanyl, they could potentially overdose, which could be fatal.
How Does Withdrawal Work
If you use opiates for an extended period of time, your body becomes desensitized to the drug. This means youll need more of it to feel its effects.
Extended use of opiates changes the structure of nerve cells in your brain. These cells will begin to need the drug just to function properly. When you stop using opiates abruptly, your body will react, leading to symptoms of withdrawal.
Opiate withdrawal occurs in two phases. The first phase includes a number of symptoms, such as:
- rapid heartbeat
These initial phases, which can last anywhere from a week to a month, can be followed by long-term withdrawal symptoms. Long-term symptoms are often less physical in nature and may involve emotional or behavioral issues.
Don’t Miss: Chc Addiction Services Akron Ohio
Prescription Opioids & Illicit Use
Opioids are legally prescribed medications used to manage or treat pain. Opioids can be addictive and an addiction to opioids is known as an Opioid Use Disorder
Prescription opioids are used to relieve pain, but they can also cause feelings of relaxation or intense euphoria, especially when misused.3, 4, 5
In addition to blocking pain signals, opioids also release large amounts of dopamine. This release can strongly reinforce the act of taking the drug and may cause the user to want to repeat the experience.6
Opioids alter the brains natural reward system, making it difficult to stop using.5 Physical dependence often makes it even harder to quit using, as the user has to take the drug to avoid the severe negative effects that occur during withdrawal.5
You May Like: Am I Addicted To Benzos
What You Need To Know
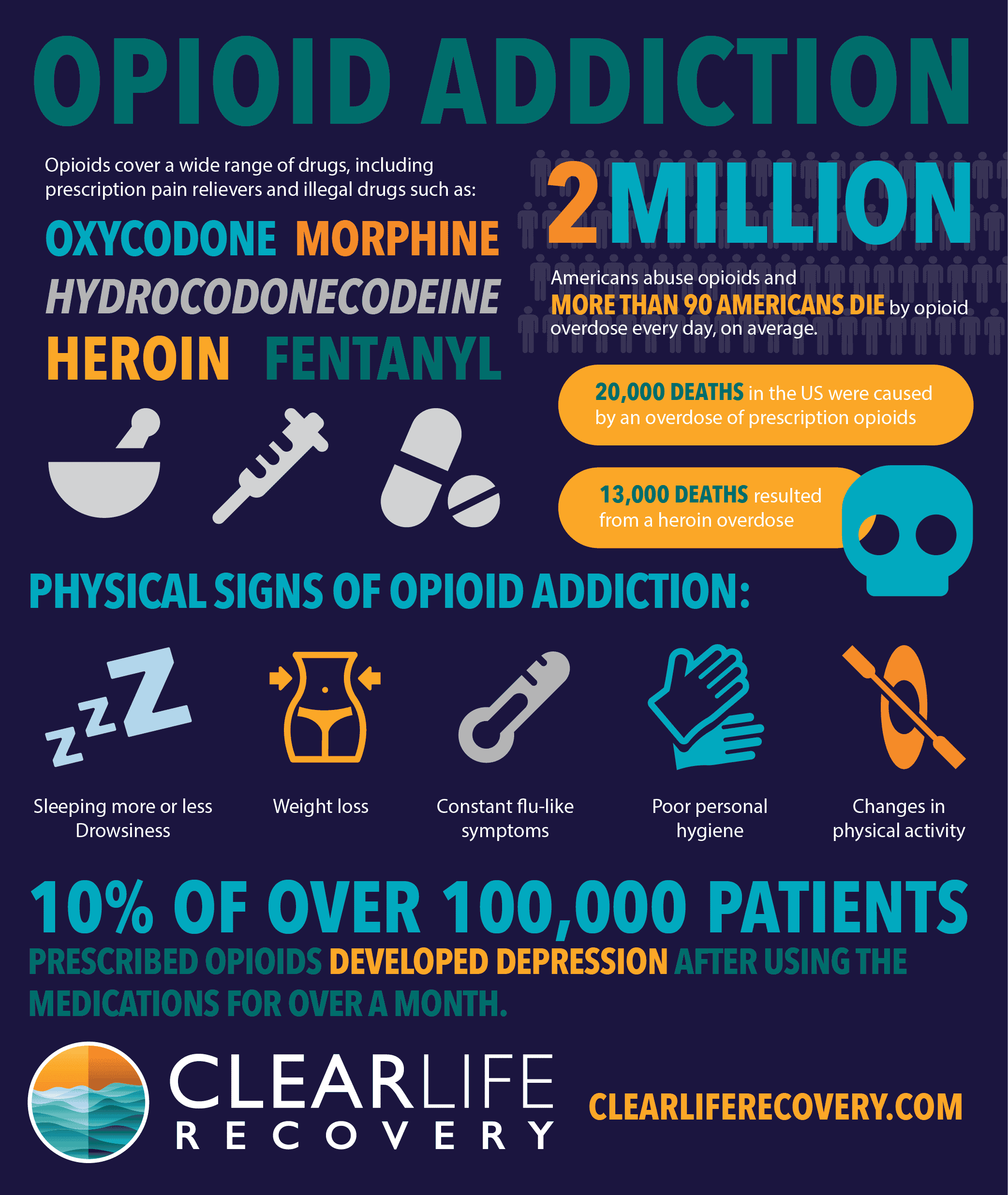
- Opioid addiction is a serious medical condition.
- Though the cause of OUD is not known, people may take opioids in an unhealthy way to achieve euphoria or to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
- Signs and symptoms of opioid use disorder include craving, risky use and withdrawal symptoms if the opioid is discontinued. If not treated, opioid use disorder can lead to overdose and death.
- Treatment, including drugs that can ease craving and help people discontinue opioid use, can help manage opioid use disorder.
Recommended Reading: Am I Addicted To Anxiety
How Do Opioids Affect The Brain
When an individual takes an opioid, they may feel a variety of effects, including drowsiness, relaxation, and slowed breathing.3 Many people also experience a rush of pleasure, also referred to as euphoria, that they find intensely rewarding.3
Opioids bind to specific receptors in the brain and disrupt the pain signals transmitted between the body and the brain, dulling the perception of painful stimuli.4 Opioids also increase the activity of dopamine, a brain-signaling molecule with an important role in reward and reinforcing behaviors.5 This release of dopamine is associated with producing pleasure, leading to repeated drug use.3 Dopamine helps to reinforce pleasurable activities, such as exercising, engaging in a fun hobby, and spending time with friends and loved ones. So, in a sense, when dopamine is released as a result of an opioid, the drug tells the brain to continue behaving in the same way, which is a contributing factor to what makes opioids addictive.3
How Are Behavioral Therapies Used To Treat Drug Addiction
Behavioral therapies help patients:
- modify their attitudes and behaviors related to drug use
- increase healthy life skills
- persist with other forms of treatment, such as medication
Patients can receive treatment in many different settings with various approaches.
Outpatient behavioral treatment includes a wide variety of programs for patients who visit a behavioral health counselor on a regular schedule. Most of the programs involve individual or group drug counseling, or both. These programs typically offer forms of behavioral therapy such as:
- cognitive-behavioral therapy, which helps patients recognize, avoid, and cope with the situations in which they are most likely to use drugs
- multidimensional family therapydeveloped for adolescents with drug abuse problems as well as their familieswhich addresses a range of influences on their drug abuse patterns and is designed to improve overall family functioning
- motivational interviewing, which makes the most of people’s readiness to change their behavior and enter treatment
- motivational incentives , which uses positive reinforcement to encourage abstinence from drugs
Also Check: How To Control Addictive Personality
What Is Suboxone And How Does It Work
Suboxone, a combination medication containing buprenorphine and naloxone, is one of the main medications used to treat opioid addiction. Using medications for opioid use disorder is known as MOUD. Use of MOUD has been shown to lower the risk of fatal overdoses by approximately 50%. It also reduces the risk of nonfatal overdoses which are traumatic and medically dangerous.
Suboxone works by tightly binding to the same receptors in the brain as other opiates, such as heroin, morphine, and oxycodone. By doing so, it blunts intoxication with these other drugs, it prevents cravings, and it allows many people to transition back from a life of addiction to a life of normalcy and safety.
A key goal of many advocates is to make access to Suboxone much more widely available, so that people who are addicted to opiates can readily access it. Good places to start are in the emergency department and in the primary care doctors office. More doctors need to become “waivered” to prescribe this medication, which requires some training and a special license.
The vast majority of physicians, addiction experts, and advocates agree: Suboxone saves lives. The U.S. Government has recently been lightening up on the requirements needed for doctors and nurses to “get waivered” in an urgent attempt to increase the availability of Suboxone prescribers, as the number of opioid deaths keeps rising.
Development Of Other Health Issues
âProlonged codeine abuse may contribute to lung infections, sleep disorders, irregular heart rate, and in some cases, brain damage.â Sean Ormond, MD at Atlas Pain Specialists, tells WebMD Connect to Care.
âWhile any one of these symptoms can indicate an unhealthy relationship with codeine, a combination of these symptoms is even more telling.â continues Parmar. âIf you have increased your dosage of codeine over time without a valid medical reason to do so, you may be developing a codeine addiction. If you regularly âforgetâ to eat meals or eat very small portions, you could be experiencing codeine effects. And if you regularly use other drugs like alcohol or marijuana to âboostâ your codeine experience, it could be a sign of a larger problem. These are signs that you have a potential codeine addiction.â
Don’t Miss: How To Avoid Addiction To Drugs
Myth #: Its As Easy To Overdose On Suboxone As It Is To Overdose With Other Opiates
Reality: It is extremely difficult to overdose on Suboxone alone. It is much more difficult to overdose on Suboxone compared to other opiates, because Suboxone is only a partial opiate receptor agonist, so there is a built-in “ceiling” effect. This means there is a limit to how much the opioid receptors can be activated by Suboxone, so there isnt as great a risk of slowed breathing compared with potent opiates such as heroin, oxycodone, or morphine. When people do overdose on Suboxone, it is almost always because they are mixing it with sedatives such as benzodiazepines, medicines that also slow breathing.
Medications That Can Be Used To Treat Opioid Use Disorder
While taking medications used to treat opiate addiction, you will not experience the usual feelings of euphoria that opiates provide instead, youll feel more like yourself and wont need to go through a difficult withdrawal period from these drugs. Some help alleviate the strong cravings for opiates that persist, while others block the effects of opiates should you relapse.
These medications include:
Also Check: How To Withdraw From Tramadol Addiction
When To Contact A Medical Professional
If you or someone you know is thinking about suicide, call or text 988 or chat 988lifeline.org. You can also call 1-800-273-8255 . The 988 Suicide and Crisis Lifeline provides free and confidential support 24/7, anytime day or night.
You can also call 911 or the local emergency number or go to the hospital emergency room. DO NOT delay.
If someone you know has attempted suicide, call 911 or the local emergency number right away. DO NOT leave the person alone, even after you have called for help.
What Medications Are Used In Treatment

Medical professionals at Gateway Foundation can recommend and administer medications such as Vivitrol or Suboxone to help you through the recovery process. While not a substitute for long-term treatment, these medicines can help patients achieve milder withdrawal symptoms and safely taper down the opioids in their system.
Also Check: What Types Of Addictions Are There
Psychological Treatments For Opioid Addiction
In the last few decades, psychological treatments have become more sophisticated. The approaches focus on every stage of overcoming opioid addiction from making the decision to change and quitting or reducing opioid use to becoming abstinent and avoiding relapse.
There are different approaches, but each should be tailored to meet the individual needs of the person with opioid use disorder.
Getting Help For Opiate Addiction
Opiates consist of a group of prescription medications usually issued to patients after surgery, injury, or the presentation of a chronic condition. The problem with opiates is that it is highly addictive and habit-forming. When you start using medication and experience relief, the body begins to depend on it to feel relaxed and good. The more you use, the more tolerant you become, which means you need to increase the amount of substance to reach the original pain-relieving effect.
Unfortunately, tolerance also leads to withdrawal when you quit using opiates. You may find yourself craving the drug when youre not actively using it. Your health is affected by dizziness, chronic nausea, slow respiration, and the inability to manage the underlying cause for pain properly.
When your drug-seeking behavior spirals out of control to the point that you neglect your family, friends, work, and responsibilities to get more of the substance, it is time to find professional addiction treatment. The clinical signs of addiction include tolerance and withdrawal, hiding the habit, seeking multiple prescriptions to maintain the pattern, and continued use of the drug despite experiencing negative consequences.
If you need opiate addiction treatment, speak to us at United Recovery. We specialize in rehabilitation for prescription medication, including opiates. Our team is ready to support you with the professional care you need to overcome addiction.
You May Like: What Is An Addiction Specialist
What Are The Symptoms Of Opioid Withdrawal
The symptoms you experience will depend on the level of withdrawal you are experiencing. Also, multiple factors dictate how long a person will experience the symptoms of withdrawal.
Because of this, everyone experiences opioid withdrawal differently. However, theres typically a timeline for the progression of symptoms.
Early symptoms typically begin in the first 24 hours after you stop using the drug, and they include:
Its important to remember that different drugs remain in your system for different lengths of time and this can affect withdrawal onset.
The amount of time your symptoms last depends on the frequency of use and severity of the addiction, as well as individual factors like your overall health.
For example, heroin is typically eliminated from your system faster, and symptoms will start within 12 hours of last use. If youve been on methadone, it may take a day and a half for symptoms to begin.
Some specialists point out that recovery requires a period of at least 6 months of total abstinence, during which the person may still experience symptoms of withdrawal.
This is sometimes referred to as protracted abstinence. Its important to discuss ongoing symptoms with a healthcare professional.
Addressing Myths About Medications
Methadone and buprenorphine DO NOT substitute one addiction for another. When someone is treated for an opioid addiction, the dosage of medication used does not get them highit helps reduce opioid cravings and withdrawal. These medications restore balance to the brain circuits affected by addiction, allowing the patients brain to heal while working toward recovery.
Diversion of buprenorphine is uncommon when it does occur it is primarily used for managing withdrawal.11,12 Diversion of prescription pain relievers, including oxycodone and hydrocodone, is far more common in 2014, buprenorphine made up less than 1 percent of all reported drugs diverted in the U.S.13
Recommended Reading: How Many People Are Addicted To Oxycodone
Sbirt: Screening Brief Intervention And Referral To Treatment
Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment is an evidence-based practice used to identify, reduce, and prevent problematic use and dependence on alcohol and other substances. The SBIRT model was impelled by an Institute of Medicine recommendation that called for community-based screening for health risk behaviors, including substance use.
ScreeningA health care professional assesses a patient for risky substance use behaviors using standardized screening tools. Screening can occur in any health care setting.
Brief InterventionA health care professional engages a patient showing risky substance use behaviors in a short conversation, providing feedback and advice.
Referral to TreatmentA health care professional provides a referral to brief therapy or additional treatment to patients who screen in need of additional services.
Data from SAMHSA-HRSA Center for Integrated Health Solutions. SBIRT: Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment. Available at: . Retrieved March 20, 2017.
Opioid Crisis In America
The opioid addiction crisis in the United States is one of the most significant public health emergencies in this generation. Opioids are a class of drugs that include fentanyl which the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has classified as the most commonly used drug in overdoses, the illegal drug heroin and pain relievers available legally by prescription, such as oxycodone , hydrocodone , codeine, morphine and others.
With its hospital-wide dedication to opioid addiction eradication, supported by a full-service Behavioral Health Services and Addiction Treatment Services, Denver Health is working in partnership with the City of Denver on a five-year plan to directly confront this national health challenge.
Denver Health joins the City of Denver alongside more than 100 governmental agencies and community organizations in its Opioid Response Strategic Plan, designed to:
- Prevent Substance Abuse and Misuse
- Improve Treatment Access and Retention
Read more on Denver Health and its partnership with the City of Denvers strategic plan.
Read Also: What Is Drug Addiction Definition
Buprenorphine Is Taken Alone Or Combination Buprenorphine & Naloxone
It is the latest kind of drug that helps in detoxification from the addiction to opioids. It activates the opioid receptors which reduce the craving for drugs preventing withdrawal.
Naloxone prevents medication misuse. Subutex is generally used for detoxification of acute opiate while the use of Suboxone is either for acute detoxification or for maintenance and prevention of opioid relapse.
One of the studies published in JAMA Psychiatry , the results found that the use of buprenorphine taper in combination with naltrexone for 4 weeks maintenance treatment enhanced abstinence rates
Read Also: How Do You Know If You Have An Addiction
What Are Some Commonly Used Opiates

Tramadol
Tramadol is a prescription opioid painkiller that doctors usually use to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. While it is considered one of the safer kinds of opiate, it is commonly abused because of its pleasurable effects.
While a high dose of tramadol can give you feelings of euphoria, constant use is hazardous to health. Tramadol abuse can lead to seizures, convulsions, and problems breathing.
Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone medication is the most commonly prescribed medicine in the United States. It is also an opiate with addictive properties. Like most opiates, if you take it in high doses, you experience feelings of euphoria and relaxation.
Doctors usually prescribe hydrocodone as a pain reliever. Even when used exactly as prescribed, there is still a risk of addiction. If you take the drug for its pleasurable effects, the risk of addiction is much higher.
Also Check: Treatment Options For Drug Addiction
