Cocaine Research Reportwhat Are Some Ways That Cocaine Changes The Brain
Use of cocaine, like other drugs of abuse, induces long-term changes in the brain. Animal studies show that cocaine exposure can cause significant neuroadaptations in neurons that release the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate.9,10 Animals chronically exposed to cocaine demonstrate profound changes in glutamate neurotransmissionincluding how much is released and the level of receptor proteinsin the reward pathway, particularly the nucleus accumbens. The glutamate system may be an opportune target for anti-addiction medication development, with the goal of reversing the cocaine-induced neuroadaptations that contribute to the drive to use the drug.9
Chronic cocaine exposure affects many other areas of the brain too. For example, animal research indicates that cocaine diminishes functioning in the orbitofrontal cortex , which appears to underlie the poor decision-making, inability to adapt to negative consequences of drug use, and lack of self-insight shown by people addicted to cocaine.12 A study using optogenetic technology, which uses light to activate specific, genetically-modified neurons, found that stimulating the OFC restores adaptive learning in animals. This intriguing result suggests that strengthening OFC activity may be a good therapeutic approach to improve insight and awareness of the consequences of drug use among people addicted to cocaine.13
What Part Of The Brain Causes Addiction
Addiction is a complex disease impacting the function of the brain. The part of the brain that causes addiction is called the mesolimbic dopamine pathway. It is sometimes called the reward circuit of the brain. Lets take a deeper look into the causes of addiction and how this area of the brain is impacted.
Addiction can have a devastating effect on the brain. Not only can it change the way the brain functions, but it can also damage the cells. Over time, this can lead to problems with memory, decision making, and emotional control. It can also increase your risk for other mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. If you or someone you know is struggling with addiction, its important to get help. There are many treatment options available, and with the right support, you can overcome addiction and reclaim your life.
At San Antonio Recovery Center, we focus on more than just treating the symptoms you have. Addiction counseling dives deep to ensure whats causing your addiction is treated properly. If you need to know more about addiction treatment, call us today at .
The Biochemistry Of Addiction
The brain responds to addiction based on a number of factors, such as the type and number of drugs used, the frequency of use, and the stage of addiction that has developed. If someone uses Cocaine, for example, they will notice a feeling of euphoria. This occurs because Cocaine is Psychoactive and impacts the area of the brain that controls pleasure and motivation. There is a short and powerful burst of dopamine, the chemical that causes many to feel euphoric. This feeling can be so intense that a strong desire to continue using may form.
The more someone abuses a drug, the more they may continue using it unless they get help overcoming a life-threatening addiction. Once the chemical has affected the brain, individuals can feel physical symptoms as well as the impact of the chemical throughout their nervous system. Symptoms can include a rapid heartbeat, paranoia, nausea, hallucinations, and other disturbing sensations the individual has little control over. He or she may become consumed with abusing the substance to maintain their habit no matter the cost. As a result of this powerful grip of substance abuse, individuals can begin acting in unrecognizable ways this may concern friends and family.
Common Questions About Rehab
You May Like: How To Support Someone With Drug Addiction
What Parts Of The Brain Are Affected By Drug Use
Drugs can alter important brain areas that are necessary for life-sustaining functions and can drive the compulsive drug use that marks addiction. Brain areas affected by drug use include:
Some drugs like opioids also disrupt other parts of the brain, such as the brain stem, which controls basic functions critical to life, including heart rate, breathing, and sleeping. This interference explains why overdoses can cause depressed breathing and death.
Understanding Addiction Reward And Pleasure In The Brain

Learning how the brain responds to pleasure has blasted the doors of addiction research wide open. Though theres still a vast amount of unknowns where the neuroscience of substance abuse is concerned, researchers understand how the brains reward and pleasure centers are hijacked by drugs and alcohol.
In addition, doctors and scientists recognize addiction as a chronic disease that changes both the function and structure of the brain.
The hold that addiction has on the brain is extreme and powerful. Without a significant disruption of the disease, such as long-term abstinence or sobriety, the risks to an individuals health are dire.
You May Like: Addiction Services Council Cincinnati Oh
What Causes Behavioral Addictions
Although there is no single cause for behavioral addictions, experts have identified numerous contributing factors. These include a genetic predisposition for addictive behaviors, changes in the structure and function of the brain, emotional trauma, and acute stress.
Many people with behavioral addictions also have co-existing conditions, such as:
The Evolution Of Motivation
Researchers have amassed a mountain of reasons to explain drug use. Leshner says that 72 risk factors have been defined, from the street price of a drug to the drug habits of the people one hangs out with. But the basic reason people use drugs isn’t complicated or mysterious. They like the way drugs make them feel.
Scientists believe, however, that the reward pathway exists for reasons more fundamental than fun. It does, after all, contain receptors, transporters, and other molecules that normally hitch up not with drugs but with the chemicals that evolution has designed for them. Scientists have known that the brain produces these natural psychoactive drugs since the 1970s, when the enkephalins, the first of the opioid peptides, were discovered. Since then, researchers have identified the natural brain analogs of all of the major drugs of abuse.
Scientists believe activation of the reward pathway is an essential spur to motivation, an incentive to learn and repeat adaptive behavior that they call reinforcement. Eating may be pleasurable, but its underlying purpose is to sustain life the pleasure that accompanies delightful flavors and full bellies is an enticement that encourages creatures to make a habit of it.
Recommended Reading: Is Nicotine Addictive By Itself
New Insights Into The Causes Of Addiction
Addiction involves craving for something intensely, loss of control over its use, and continuing involvement with it despite adverse consequences. Addiction changes the brain, first by subverting the way it registers pleasure and then by corrupting other normal drives such as learning and motivation. Although breaking an addiction is tough, it can be done.
What Does It Mean To Call Addiction A Brain Disorder
Calling addiction a brain disorder means, for one thing, that the machinery of addiction is complex and subtle, because the brain is complex and often subtle. Addiction comes about through the brains normal pathways of pleasure. It is known that addiction changes the circuitry of the brain in ways that make it increasingly difficult for people to regulate the allure of an intense chemical rush of reward.
In response to repeated use of a highly pleasurable experiencedrugs, gamblingneurons adjust their wiring to become increasingly efficient at relaying the underlying signals. They prune away their capacity to respond to other sources of reward. And neural connection to the brain centers of impulse control and decision-making is weakened. The brain is set to stay stuck in its habit.
But, unlike in disease, the brain changes that occur in addiction are not a malfunction of biology. Rather, the changes reflect the brains normal processes of changeabilitycalled neuroplasticityits capacity to change in response to every-day experience, which is the basis of all learning. Unlike other organs, the brain is designed to change, because its mission is to keep us alive, and in order to safeguard us, it needs to be able to detect and respond to the ever-changing dynamics of the real world.
It is important to know that recovery from addiction also relies on neuroplasticity. Changing behavior rewires the brain.
You May Like: Drug Addiction In The United States
The Brain Addiction And Withdrawal
As a consequence of drug addiction, the brain rewards the harmful behavior. It encourages drug addiction, keeping the individual in a cycle of highs and lows the user may feel like theyre on an emotional roller-coaster, feeling desperation and depression without their substance of abuse. Once someone suddenly stops using, there are harsh mental, physical, and emotional results. Individuals may experience distressing symptoms they cannot ignore for some substances withdrawal symptoms are generally stronger for some substances than others.
At the point of withdrawal, someone who stops using Heroin experiences intense cravings, depression, anxiety, and sweating. Much of this is due to the rewiring of the brain after extended Heroin use. In this stage, the individual may not have a full-blown addiction a tolerance or dependency may have developed, however. Over time, the high volume of chemicals floods the brain the brain correspondingly adapts to the mental effects of the substance. The brain then reduces its production of neurotransmitters, chemical messengers in the brain. Withdrawal symptoms often need professional treatment, which can significantly help reduce the chance of relapse and the risks of stroke and heart attack.
Online Addiction Counseling
Paid Advertising. We may receive advertising fees if you follow links to the BetterHelp site.
How The Brain Responds To Withdrawal
During abstinence and withdrawal, these neurotransmitters are decreased resulting in feeling pain, anxiety, and dysphoria, Dr. Fiellin says. It is these changes, as well as other neurocircuitry, that occur in the brain that may drive the person to seek out the substance just to feel normal.
When the intoxicating effects of a substance wears off, there is an increase in signaling in some circuits of the forebrain. This firing triggers cravings for the substance and drives the individual to seek the substance out.
Whats wild, is that search alone can release dopamine into the basal ganglia when someone is craving the substance. This motivates them to keep going until they find it and consume the substance.
In brains that are not addicted, these circuits in charge of desire are held in check. The prefrontal cortex, which helps us make rational decisions and regulate emotions, prevail because the individual can balance the long-term goals against immediate reward.
But, repeated substance exposure can weaken these circuits. And in that case, the desire for the substance is too strong to ignore. This is what makes it so difficult for the individual who is living with addiction to stop taking the substance despite negative experiences with the substance, or even, lack of the pleasure they once experienced.
Recommended Reading: Resources To Help With Addiction
Changes Last Long After Use
Stopping drug use doesnt immediately return the brain to normal. Some drugs have toxic effects that can kill neuronsand most of these cells will not be replaced. And while changes to connections between neurons in the brain may not be permanent, some last for months. Some research suggests the changes may even last for years.
Long-lasting brain changes can make it challenging for addicts to stay drug-free. They often experience intense cravings, leading to relapse.
How Do Drugs Affect Your Brain
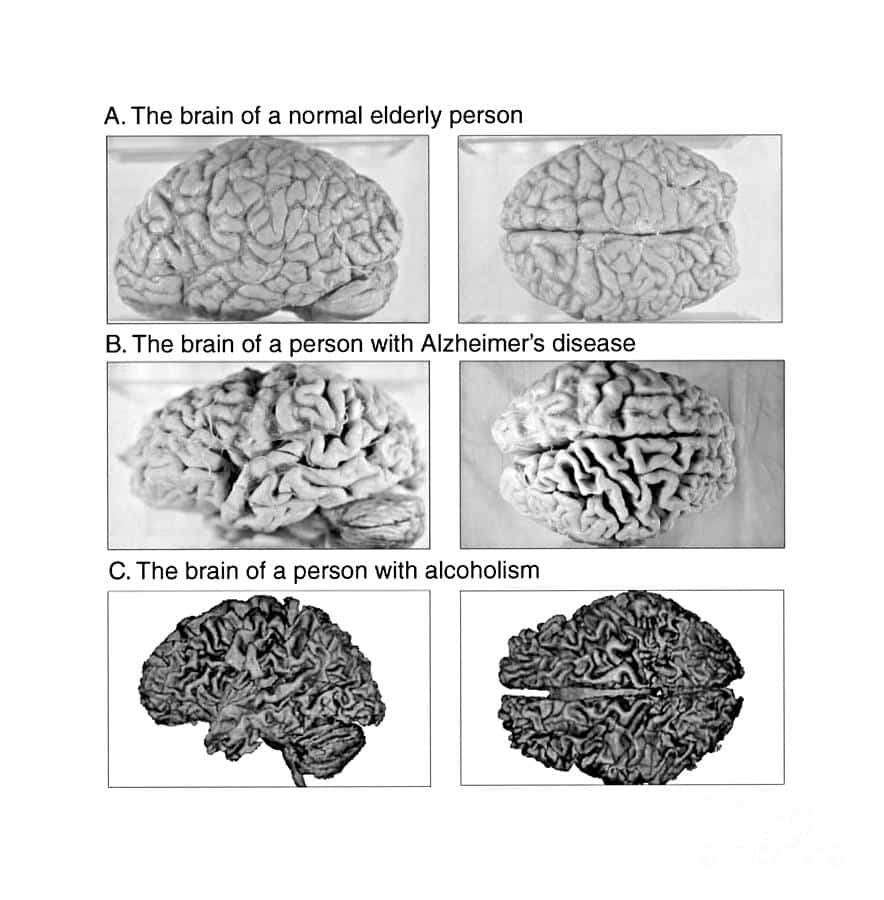
When you have a substance use disorder, your brain might not work as well as it should. Drugs can interfere with your brains normal chemistry. While you might not feel any different or notice any significant changes at first, your behavior may gradually become erratic as your brain adjusts to drug use. If your brain has been or is currently affected by drug use, you might notice changes in behavior that can include:
- Impulse control. When youre struggling with addiction, your brain tends to prompt strong impulse reactions. When this takes place, you might engage in risky behaviors.
- Emotional control. Many types of drugs can make it hard for you to experience emotions. When the high is over, your emotions might become too much to bear, causing you to lash out emotionally or turn back to drug use.
- Memory. Some drugs can affect your brains hippocampus, which allows you to learn and memorize information. When youre struggling with substance abuse challenges, you may have trouble remembering bills, important dates, meetings, work obligations, or social activities.
- Reward system. Drugs trick and rewire the brains pleasure system, making it more likely that you will take drugs again and again.
- Flexible thinking. Drugs might affect the way your brain processes information. If youre unable to take in new information, youll find it hard to learn, adapt, or change your behavior. You may also find it really difficult to overcome bad or harmful habits.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If You’re Addicted To Something
Chronic And Relapsing Developmentally
Much of the critique targeted at the conceptualization of addiction as a brain disease focuses on its original assertion that addiction is a chronic and relapsing condition. Epidemiological data are cited in support of the notion that large proportions of individuals achieve remission , frequently without any formal treatment and in some cases resuming low risk substance use . For instance, based on data from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions study , it has been pointed out that a significant proportion of people with an addictive disorder quit each year, and that most afflicted individuals ultimately remit. These spontaneous remission rates are argued to invalidate the concept of a chronic, relapsing disease .
The NESARC data nevertheless show that close to 10% of people in the general population who are diagnosed with alcohol addiction never remitted throughout their participation in the survey. The base life-time prevalence of alcohol dependence in NESARC was 12.5% . Thus, the data cited against the concept of addiction as a chronic relapsing disease in fact indicate that over 1% of the US population develops an alcohol-related condition that is associated with high morbidity and mortality, and whose chronic and/or relapsing nature cannot be disputed, since it does not remit.
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
13 September 2018
Luke Clark, Isabelle Boileau & Martin Zack
11 January 2021
Victor Pando-Naude, Sebastian Toxto, Eduardo A. Garza-Villarreal
volume 46, pages 17151723
Recommended Reading: Why Do People Get Addicted To Meth
What Areas Of The Brain Influence Addiction
The brain controls temperature, emotion, decision-making, breathing, and coordination. It also impacts physical discomfort, cravings, compulsions, and behavioral habits, as well as the physical sensations in the body. When the limbic system is affected by a harmful chemical, individuals abusing substances like Benzodiazepines or Heroin can alter their brain functionality.
This happens as a result of interacting with the limbic system. The brain releases intense feel-good emotions, which affect the individuals body and mind. Individuals are drawn to drugs to support the intense feel-good emotions the brain releases, resulting in a cycle of drug use and intense highs. They take the drug primarily to feel normal.
Activation of the nucleus accumbens, a cluster of nerve cells located behind the cerebral cortex, is associated with all forms of pleasure, whether induced by drugs, monetary rewards, sexual encounters, or satisfying meals. Dopamine is released in the nucleus accumbens when someone experiences pleasure
Because this region of the brain is engaged consistently when people experience pleasure, scientists refer to it as the pleasure center. As a result, all drugs of abuse, from nicotine to heroin, deliver a particularly intense dopamine boost in the nucleus accumbens. Drug addiction, therefore, is associated with how fast dopamine is released, how intensely it is released, and how reliably it is released.
How Neurotransmitters Work
Time for the neuroscience lesson. Within the midbrain youll find tiny structuressubstantia nigra and ventral tegmental areathat release the neurotransmitter . Just to back up, neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that help carry information through the brain cells or neurons to other neurons. Each neurotransmitter has receptors that accept its message. Dopamine has five of these receptors in the central nervous system and the most abundant helps regulate the reward system, motor activity, memory, and learning receptors.
Read Also: How To Fix An Addictive Personality
This Is Your Brain On Lsd
Last year a team of researchers published the first brain scans of people on LSD that use modern neuroimaging techniques. The results showed a surprisingly strong connection between how people experience an acid trip, and what is physically going on in their brains. Compared to a placebo group, participants on LSD had more blood flow to their visual cortex the visual processing center and way more connectivity between the visual cortex and the rest of the brain. The times when this activity was strongest was when people said they were experiencing visual hallucinations.
The study also found a correlation between peoples experience of ego-dissolution being at one with the universe and decreased connectivity between two brain regions, the parahippocampus and the retrosplenial cortex.
There has been a resurgence of interest in recent years in the potential therapeutic benefits of LSD. When taken in controlled circumstances, the drug appears to help people overcome anxiety and addictions.
Why Do Different Theories Of Addiction Exist
Different theories of addiction exist as it is the only disease that can be self-diagnosed and is treatable should the individual put the work in. So one would say its not a disease as we dont choose to have cancer but we choose to be an addict. Unless one is an addict, they really cant speak to how it feels to live in turmoil and with this constant obsession in your brain. There is a level of self-sabotage and the cycle repeats itself. The addict wants to get out of it, but the obsession of the mind takes over and so the cycle repeats itself. Shameful things are done and instead of knowing how to fix those things, the addict uses again to numb the feelings of the shameful behavior they created. It is a level on insanity once doesnt know unless they have experienced it.
Don’t Miss: How To Quit Cough Syrup Addiction
