Internal Effects Of Addiction On The Body
Because of the effects addiction has on the bodys major organs, it can lead to heart disease, liver failure, some types of cancer, kidney failure, overdose, and even death. Drugs and alcohol can cause chronic heart problems and diseases that could result in heart attacks, high blood pressure, and an irregular heartbeat. These heart complications can be fatal. Addiction can also contribute to cirrhosis of the liver, cancer, and organ damage or failure. Drug and alcohol use also weakens the immune system, which can make a person prone to many diseases and viruses.
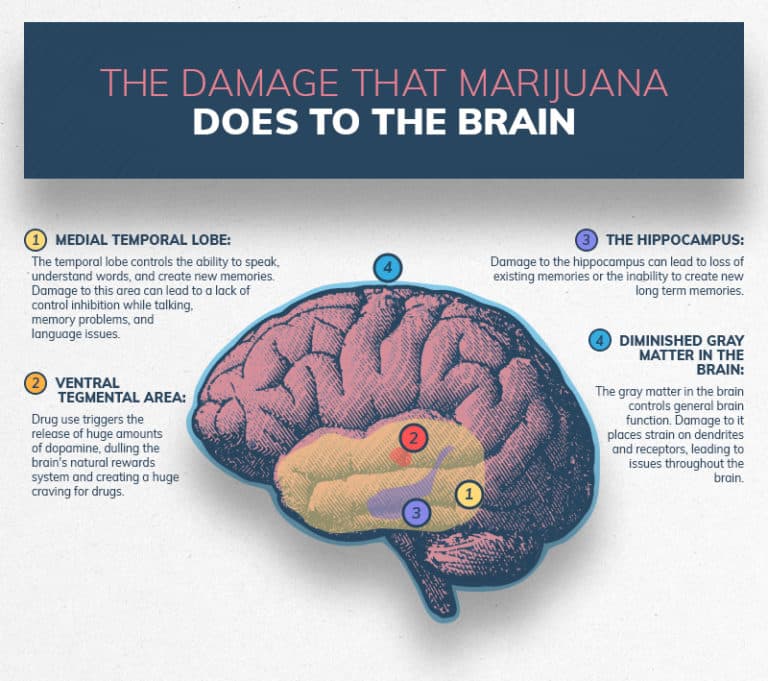
Treatment Of Shatter Dependence And Addiction
While shatter addiction or dependence is rare, it can affect some people and once it has taken hold it can be difficult to overcome alone. Intense and cravings can cause many people attempting to quit alone to relapse. In these cases, marijuana addiction treatment in an outpatient or inpatient setting is recommended.
While there are no medications currently used to treat marijuana addiction, a combination of talking therapies such as CBT, detoxification, and support groups such as NA are proven to be the most effective forms of treatment.
If you or someone you know is struggling with shatter addiction or any other form of THC dependency, then visit our rehab directory to find available treatment near you.
Resources:
Loflin, M., & Earleywine, M. . A new method of cannabis ingestion: The dangers of dabs? Addictive Behaviors, 39, 14301433.
The Top Tools Being Utilized For Research On The Brain In Recovery
Functional brain measurement techniques:
Methods that provide dynamic physiological information about brain function/activity. Functional imaging techniques allow scientists to measure the contributions of various structures to specific psychological processes . Commonly obtained while participants complete tasks, functional images offer insight to the brain regions that are activated, or recruited, to perform a given task. Atypical brain function in patient populations can include reduced neural activation or a different pattern of brain activation as compared to healthy control populations.
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
-
Also known as a functional MRI , this imaging technique measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow and oxygenation.
- Numerous studies utilizing functional magnetic resonance imaging have shown that drug cues elicit increased regional blood flow in reward-related brain areas among addicted participants that is not found among normal controls
See the fMRI in action:
Structural brain measurement techniques:
Imaging techniques that allow one to examine the brains anatomical structure. Structural imaging provides static information, and is analogous to taking a photograph of the brain. These images permit evaluation of gross anatomical abnormalities, including tissue atrophy and reduced white matter integrity .
Read Also: National Alcohol And Drug Addiction Recovery Month
External Effects Of Addiction On The Body
Addiction not only causes internal changes, but also physical changes in appearance. It can alter a persons skin, hair, nails, weight, and teeth. Acne and skin lesions can be a common effect of addiction, as well as baldness or male pattern hair growth in women. Addiction can also cause jaw and teeth issues such as cavities and gum disease. When it comes to how substance abuse affects the body, these changes can cause struggles in day-to-day life, and its important to seek help if youre struggling.
Can Neurological Complications Arise From Withdrawal
Neurological complications may result from withdrawal of certain substances. Medically supervised detox may help to reduce the likelihood or severity of many of these risks. You will receive constant monitoring and supervision as well as medication to address any symptoms or complications that may arise as a result of withdrawal.21
Withdrawal from substances like alcohol and benzodiazepines may also present a risk of withdrawal seizures.21,22 top Seizures can be dangerous because you can suffer from falls or injuries or develop a potentially lethal condition known as status epilepticus, which is when you have a seizure that lasts more than 5 minutes or when seizures occur too often in too short a time span.23
Read Also: Can Cbd Help With Addiction
How Long Does It Take The Brain To Recover From Addiction
Alcohol and drugs affect the brains neurotransmitters and neural pathways. At the same time, the brain strives to maintain balance. As a result, when drugs and alcohol change the brains chemistry, the brain adapts. Once the adaptation becomes the norm, the brain will want to correct an imbalance when the drug is no longer present by taking the drug again. Over time, substance use disorder changes both the brains structure and how it functions.
The brain has billions of neurons, which connect via neural pathways. As children develop and learn, their brains create and change these pathways, a process known as neuroplasticity, with relative ease. At approximately age twenty-five, the brain has developed the majority of its neural pathways its plasticity is significantly reduced.
The brain uses neural pathways as efficiently as possible, allowing repetitive tasks to become automatic or habitual. The frequent use of the same circuits embeds them deeper into the brain, making it more difficult to alter their routes. Imagine dragging a scissors blade across cardboard along the same line over and over the groove gets more pronounced. Fortunately, the brain is more flexible than cardboard. Although adults need more time and effort to change neural pathways than a child does, adults can change their brains.
Why Heroin Causes Dependence
When opioid receptors adapt to heroin and become less responsive, other changes occur that make the brain rely on the drug to function normally. This is called dependence. Without heroin, the opioid receptors of a dependent person act abnormally. This abnormal brain activity causes heroin withdrawal symptoms.
You May Like: Effects Of Social Media Addiction
Cocaine And Brain Aging
As a person grows older, their brain will naturally change and begin to lose gray matter. In a healthy brain, this is a decades-long process, and it does not appear until a person has reached older adulthood. Memory problems, changes in cognitive ability, and even dementia are linked to reduction of gray matter.
A recent study through the University of Cambridge examined the aging of the brain in people who abused cocaine and those who had no previous history of substance abuse. The group found that the average brain normally loses 1.69 milliliters of gray matter per year however, people who had abused cocaine in the past, or who were currently cocaine-dependent, doubled the rate of gray matter loss, for an average of 3.08 milliliters per year.2
Another study, conducted by Johns Hopkins University, found that cocaine may cause brain cells to cannibalize themselves.3 The study describes cocaine triggering autophagy in neurons in mice, or the process of the cells eating themselves from the inside out. The cells threw out useful resources during metabolism, leading to a stress reaction of cannibalizing other internal cell structures. Mice whose mothers had been fed cocaine during pregnancy, but who were not cocaine-dependent themselves, also showed this phenomenon.
Factors That Contribute To Addiction
Why one person may become addicted to a substance where another, with the same consumption habits, does not remain one of the more vexing questions about substance use and addiction. Substance use can progress due to several factors that influence substance-seeking behaviors. These factors include:
- Genetics and biology. Family history of addiction and other still unknown biological factors can predispose someone to addiction.
- Age of onset. The earlier the substance use begins, the higher the chances that the individual will develop a substance use disorder later in life.
- Personality traits. The persons unique psychological makeup, coping skills, temperament, resilience capacity, and personality all factor in.
- Environmental. Family dynamics and early childhood experiences shape a persons mental wellbeing. A history of abuse, neglect, attachment disorder, and family discord can set the stage for a substance use disorder later in life.
- Negative life events. Experiencing trauma or the loss of a parent or sibling, or any devastating life event can lead someone to begin self-medicating symptoms of depression or anxiety.
There is still much to be learned about why some people develop addictions while others do not. The more that is revealed through neurobiology, the clearer our understanding becomes about the prevention, causes, and treatment of substance use disorders.
Recommended Reading: How Long To Get Back To Normal After Opiate Addiction
What Does It Mean To Call Addiction A Brain Disorder
Calling addiction a brain disorder means, for one thing, that the machinery of addiction is complex and subtle, because the brain is complex and often subtle. Addiction comes about through the brains normal pathways of pleasure. It is known that addiction changes the circuitry of the brain in ways that make it increasingly difficult for people to regulate the allure of an intense chemical rush of reward.
In response to repeated use of a highly pleasurable experiencedrugs, gamblingneurons adjust their wiring to become increasingly efficient at relaying the underlying signals. They prune away their capacity to respond to other sources of reward. And neural connection to the brain centers of impulse control and decision-making is weakened. The brain is set to stay stuck in its habit.
But, unlike in disease, the brain changes that occur in addiction are not a malfunction of biology. Rather, the changes reflect the brains normal processes of changeabilitycalled neuroplasticityits capacity to change in response to every-day experience, which is the basis of all learning. Unlike other organs, the brain is designed to change, because its mission is to keep us alive, and in order to safeguard us, it needs to be able to detect and respond to the ever-changing dynamics of the real world.
It is important to know that recovery from addiction also relies on neuroplasticity. Changing behavior rewires the brain.
Competition Between Memory Systems
Although it is possible that addictive drugs enhance habit memory directly by enhancing function of the DLS , another possibility is that drugs of abuse enhance habit memory indirectly via modulation of other memory systems. This alternative mechanism invokes the hypothesis that in some learning situations, memory systems compete for control of learning and that by impairing the function of one memory system, function of another intact system might be enhanced . Notably, the hippocampus and DLS might sometimes compete for control of learning, whereby lesion of the hippocampus enhances DLS-dependent memory function . Competitive interactions can also be demonstrated in dual-solution tasks, when impairing one memory system results in the use of a strategy mediated by another intact system. For instance, animals given DMS lesions display DLS-dependent habitual responding for food reward in instrumental learning tasks .
Read Also: Am I Addicted To Video Games
Which Brain Chemical Is Associated With Addiction
The brain chemical that plays a starring role in addiction is the neurotransmitter dopamine. Addictive drugs such as cocaine, heroin, and many othersand eventually, just the anticipation of consuming those agentscause a flood of dopamine to be released in the nucleus accumbens of the brain, creating an intensely pleasurable sensation. That pleasurable reward reinforces the behavior, motivating the user to seek the experience again and again. Dopamine is released in response to sex, accomplishment, winning, and other positive experiences, creating the sensation of reward and motivating the desire for repetition of the experience, but the dopamine response to drugs like heroin and cocaine is especially fast and intense.
The neurotransmitter glutamate is also involved in addiction. Widely distributed in the brain, its general role is to activate the firing of neurons its called an excitatory neurotransmitter. Glutamate helps mediate the rewarding effects of drugs of abuse and speeds the hard-wiring of substance response into the brain.
Whos Most Likely To Become Addicted

Each personâs body and brain are different. People also react differently to drugs. Some love the feeling the first time they try it and want more. Others hate it and never try again.
Not everyone who uses drugs becomes addicted. But it can happen to anyone and at any age. Some things may raise your chances of addiction, including:
- Family history. Your genes are responsible for about half of your odds. If your parents or siblings have problems with alcohol or drugs, youâre more likely as well. Women and men are equally likely to become addicted.
- Early drug use. Childrenâs brains are still growing, and drug use can change that. So taking drugs at an early age may make you more likely to get addicted when you get older.
- Mental disorders. If youâre depressed, have trouble paying attention, or worry constantly, you have a higher chance of addiction. You may turn to drugs as a way to try to feel better. A history of trauma in your life also makes you more likely to have addiction.
- Troubled relationships. If you grew up with family troubles and arenât close to your parents or siblings, it may raise your chances of addiction.
Don’t Miss: What Is Drug Dependence And Addiction
The Effects On The Brain
Addiction affects the brain on many levels. Alcohol, nicotine, stimulants, opioids, and sedatives enter the brain and circulation upon consumption. Once a chemical reaches the brain, it interacts with the brains limbic system to produce intense feelings of well-being, altering the body and mind of the person.
Individuals continue to take drugs to sustain the extreme positive feelings released by the brain, thus perpetuating a cycle of drug use and intense highs. They eventually take the drug to feel normal.
Addiction occurs when the brain continues to crave the feeling of reward obtained by using substances. Because of this effect, many users start misusing the substance, leading to various euphoric sensations and bizarre behavioral patterns.
The more a person misuses a substance, the more likely they will continue using it unless they obtain assistance to overcome a potentially fatal addiction. They may become fixated on using it to continue their habit, regardless of the cost. Due to drug abuses overwhelming hold, people may begin to behave in unrecognizable ways, which may cause anxiety among friends and family.
What Part Of The Brain Causes Addiction
Addiction is a complex disease impacting the function of the brain. The part of the brain that causes addiction is called the mesolimbic dopamine pathway. It is sometimes called the reward circuit of the brain. Lets take a deeper look into the causes of addiction and how this area of the brain is impacted.
Addiction can have a devastating effect on the brain. Not only can it change the way the brain functions, but it can also damage the cells. Over time, this can lead to problems with memory, decision making, and emotional control. It can also increase your risk for other mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. If you or someone you know is struggling with addiction, its important to get help. There are many treatment options available, and with the right support, you can overcome addiction and reclaim your life.
At San Antonio Recovery Center, we focus on more than just treating the symptoms you have. Addiction counseling dives deep to ensure whats causing your addiction is treated properly. If you need to know more about addiction treatment, call us today at .
Also Check: Treatment Plan For Drug And Alcohol Addiction
Overcoming Drug Abuse At Renaissance Recovery
If you have been abusing any kind of substance, whether alcohol, prescription opioids or benzos, or illicit drugs, research shows intensive outpatient programs are typically just as effective as residential rehab for treating most addictions.
Here at Renaissance Recovery, we have a variety of personalized outpatient treatment programs to help you combat your substance use disorder, as well as any co-occurring mental health disorders.
Through a combination of medication-assisted treatment and psychotherapy like CBT or DBT, youll explore the root cause of your addiction, while negotiating detox and withdrawal as seamlessly as possible. Youll also have counseling both individual and group as well as holistic therapies, experiential adventure therapies, and vocational development programs.
All you need is the commitment to sobriety and the willingness to reach out to admissions right now at . Well guide you every step of the way through your ongoing recovery journey.
Drug Addiction Recovery And Strengthening Your Brain
Its no secret that drugs have the potential to damage your brain. They can disrupt your brains delicate balance and destroy neural connections. But hope isnt lost. The brain is really good at rewiring itself and modifying its connections. In addition to that, you can use other parts of your brain to maintain key functionality while you recover from addiction.
Here at Meta Addiction Treatment, our staff members know what its like to overcome addiction challenges. Many of them are in active recovery and are ready and willing to help you recover from drug addiction and strengthen your brain. You need to take the first step. Contact our office today at 855-629-3757 if youre ready to begin, continue, or have questions about the recovery process. We designed our treatment programs for real people seeking real recovery.
Read Also: Is Ativan Addictive In Small Doses
How Can Addiction Affect The Brain But Not Be A Brain Disease
Addiction corrupts the ability to make choices. Addiction brings about changes in the brain, but those changes do not reflect a pathological process. The pathways to addiction can be difficult to understand, because substance abuse, as a result of the intense burst of pleasure it brings, rapidly rewires the circuitry of the brain to become highly efficient at drug wanting and seeking.
At first glance, the fact that addiction shifts the way the brain works lends credibility to the idea of a disease. However, the brain alterations reflect the normal capacity of the brain to change in response to experience. That capacity is called neuroplasticity, and it is the basis of all learning and change. Unlike other organs, the brain is designed to change.
